最简单的模式,C/S模式实现聊天室
从半双工开始,何谓半双工?半双工即是说双方可以互发消息,但一次只能一个用户发送。
只要稍微会点socket编程的人都会觉得很简单,所以过过场,直接上代码。
服务器端代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
from socket import *from time import ctime HOST = ''PORT = 4568BUFSIZE = 1024ADDR = (HOST,PORT) tcpSerSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)tcpSerSocket.bind(ADDR)tcpSerSocket.listen(5) while True: print('waitint for connection...') tcpCliSocket, addr = tcpSerSocket.accept() print('connecting from: ', addr) while True: data = tcpCliSocket.recv(BUFSIZE) if not data: break print data msg = raw_input('>') tcpCliSocket.send('[%s] %s' % (ctime(), msg)) tcpCliSocket.close()tcpSerSocket.close() |
客户端代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
from socket import * HOST = 'localhost'PORT = 4568BUFSIZE = 1024ADDR = (HOST, PORT) tcpCliSocket = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)tcpCliSocket.connect(ADDR) while True: data = raw_input('>>') if not data: break tcpCliSocket.send(data) data = tcpCliSocket.recv(BUFSIZE) if not data: break print data tcpCliSocket.close() |
运行结果我就不截图了,如果还不会的就复制下来运行一遍。
上面只是最简单的入门,一点都不好使,问题多着。
下面看怎么实现全双工。全双工就是双方可任意给对方发送消息。
全双工明显要用到多线程。我们在主线程之外创建两个子线程,一个负责接收消息,另一个负责接受用户输入并发送消息。
服务器端代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
|
#coding: utf-8from socket import *from time import ctimeimport threadingfrom sys import stdout HOST = ''PORT = 21567BUFSIZE = 1024ADDR = (HOST, PORT) def Send(sck): while True: data = raw_input('>') sck.send(data) def Deal(sck, addr): while True: data = sck.recv(BUFSIZE) if data == "quit": sck.close() break str = '\nfrom' + addr[0] + ':' + data + '\n>' stdout.write(str) chatSerSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM)chatSerSock.bind(ADDR)chatSerSock.listen(5) threads = [] while True: print 'waiting for connection...' chatCliSock, addr = chatSerSock.accept() print "...connected from: ", addr t = threading.Thread(target=Deal, args=(chatCliSock, addr)) threads.append(t) t = threading.Thread(target=Send, args=(chatCliSock,)) threads.append(t) for i in range(len(threads)): threads[i].start() threads[0].join() chatCliSock.close()chatSerSock.close() |
客户端代码:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
#coding: utf8from socket import *from time import ctimeimport threadingfrom sys import stdout def Send(sck, test): while True: data = raw_input('>') sck.send(data) if data == "quit": breakdef Recieve(sck, test): while True: data = sck.recv(BUFSIZ) if data == "quit": sck.close() break str = "\nfrom server:" + data + "\n>" stdout.write(str) HOST = 'localhost'PORT= 21567BUFSIZ = 1024ADDR = (HOST, PORT)threads = [] if __name__ == "__main__": chatCliSock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM) chatCliSock.connect(ADDR) t = threading.Thread(target=Send, args = (chatCliSock, None)) threads.append(t) t = threading.Thread(target=Recieve, args = (chatCliSock, None)) threads.append(t) for i in range(len(threads)): threads[i].start() threads[0].join() chatCliSock.close() |
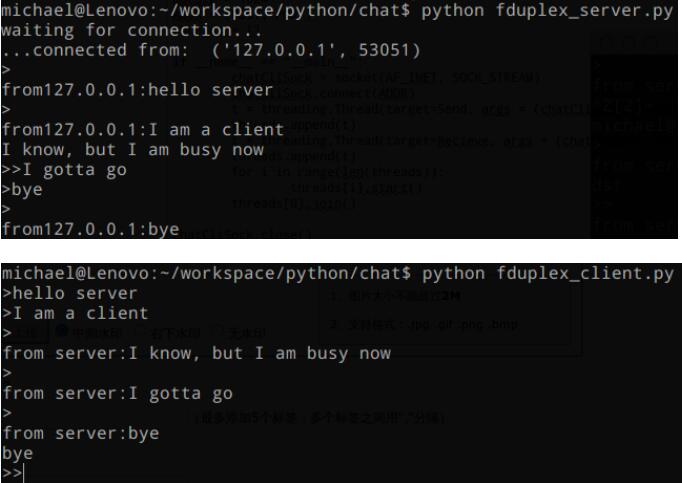
运行结果:
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/whoami021/article/details/21285421










