关于excel和shp的使用在matplotlib
- 使用pandas 对excel进行简单操作
- 使用cartopy 读取shpfile 展示到matplotlib中
- 利用shpfile文件中的一些字段进行一些着色处理
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-# @file : map02.py# @author: huifer# @date : 2018/6/28import foliumimport pandas as pdimport requestsimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport cartopy.crs as ccrsimport zipfileimport cartopy.io.shapereader as shapereadfrom matplotlib import cmfrom cartopy.mpl.ticker import longitudeformatter, latitudeformatterimport osdataurl = "http://image.data.cma.cn/static/doc/a/a.0012.0001/surf_chn_mul_hor_station.xlsx"shpurl = "http://www.naturalearthdata.com/http//www.naturalearthdata.com/download/10m/cultural/ne_10m_admin_0_countries.zip"def download_file(url): """ 根据url下载文件 :param url: str """ r = requests.get(url, allow_redirects=true) try: open(url.split('/')[-1], 'wb').write(r.content) except exception as e: print(e)def degree_conversion_decimal(x): """ 度分转换成十进制 :param x: float :return: integer float """ integer = int(x) integer = integer + (x - integer) * 1.66666667 return integerdef unzip(zip_path, out_path): """ 解压zip :param zip_path:str :param out_path: str :return: """ zip_ref = zipfile.zipfile(zip_path, 'r') zip_ref.extractall(out_path) zip_ref.close()def get_record(shp, key, value): countries = shp.records() result = [country for country in countries if country.attributes[key] == value] countries = shp.records() return resultdef read_excel(path): data = pd.read_excel(path) # print(data.head(10)) # 获取几行 # print(data.ix[data['省份']=='浙江',:].shape[0]) # 计数工具 # print(data.sort_values('观测场拔海高度(米)',ascending=false).head(10))# 根据值排序 # 判断经纬度是什么格式(度分 、 十进制) 判断依据 %0.2f 是否大于60 # print(data['经度'].apply(lambda x:x-int(x)).sort_values(ascending=false).head()) # 结果判断为度分保存 # 坐标处理 data['经度'] = data['经度'].apply(degree_conversion_decimal) data['纬度'] = data['纬度'].apply(degree_conversion_decimal) ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.platecarree()) ax.set_extent([70, 140, 15, 55]) ax.stock_img() ax.scatter(data['经度'], data['纬度'], s=0.3, c='g') # shp = shaperead.reader('ne_10m_admin_0_countries/ne_10m_admin_0_countries.shp') # # 抽取函数 州:国家 # city_list = [country for country in countries if country.attributes['admin'] == 'china'] # countries = shp.records() plt.savefig('test.png') plt.show()def gdp(shp_path): """ gdp 着色图 :return: """ shp = shaperead.reader(shp_path) cas = get_record(shp, 'subregion', 'central asia') gdp = [r.attributes['gdp_md_est'] for r in cas] gdp_min = min(gdp) gdp_max = max(gdp) ax = plt.axes(projection=ccrs.platecarree()) ax.set_extent([45, 90, 35, 55]) for r in cas: color = cm.greens((r.attributes['gdp_md_est'] - gdp_min) / (gdp_max - gdp_min)) ax.add_geometries(r.geometry, ccrs.platecarree(), facecolor=color, edgecolor='black', linewidth=0.5) ax.text(r.geometry.centroid.x, r.geometry.centroid.y, r.attributes['admin'], horizontalalignment='center', verticalalignment='center', transform=ccrs.geodetic()) ax.set_xticks([45, 55, 65, 75, 85], crs=ccrs.platecarree()) # x坐标标注 ax.set_yticks([35, 45, 55], crs=ccrs.platecarree()) # y 坐标标注 lon_formatter = longitudeformatter(zero_direction_label=true) lat_formatter = latitudeformatter() ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(lon_formatter) ax.yaxis.set_major_formatter(lat_formatter) plt.title('gdp test') plt.savefig("gdb.png") plt.show()def run_excel(): if os.path.exists("surf_chn_mul_hor_station.xlsx"): read_excel("surf_chn_mul_hor_station.xlsx") else: download_file(dataurl) read_excel("surf_chn_mul_hor_station.xlsx")def run_shp(): if os.path.exists("ne_10m_admin_0_countries"): gdp("ne_10m_admin_0_countries/ne_10m_admin_0_countries.shp") else: download_file(shpurl) unzip('ne_10m_admin_0_countries.zip', "ne_10m_admin_0_countries") gdp("ne_10m_admin_0_countries/ne_10m_admin_0_countries.shp")if __name__ == '__main__': # download_file(dataurl) # download_file(shpurl) # cas = get_record('subregion', 'central asia') # print([r.attributes['admin'] for r in cas]) # read_excel('surf_chn_mul_hor_station.xlsx') # gdp() run_excel() run_shp() |
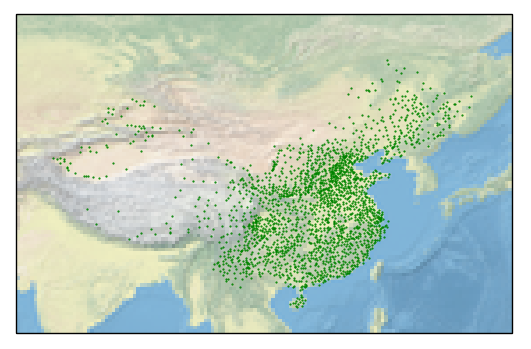

总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对服务器之家的支持。如果你想了解更多相关内容请查看下面相关链接
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/staHuri/article/details/80840339










