本文介绍了spring boot整合cucumber(bdd)的方法,分享给大家,具体如下:
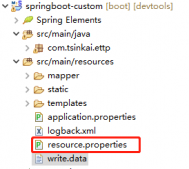
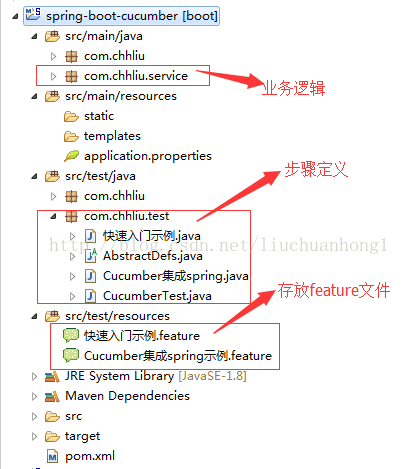
1、新建一个springboot工程工程结构如下:
2、添加pom依赖
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
|
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/pom/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/xmlschema-instance" xsi:schemalocation="http://maven.apache.org/pom/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd"> <modelversion>4.0.0</modelversion> <groupid>com.chhliu</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-cucumber</artifactid> <version>0.0.1-snapshot</version> <packaging>jar</packaging> <name>spring-boot-cucumber</name> <description>demo project for spring boot and cucumber</description> <parent> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactid> <version>1.5.6.release</version> <relativepath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <properties> <cucumber.version>1.2.4</cucumber.version> <project.build.sourceencoding>utf-8</project.build.sourceencoding> <project.reporting.outputencoding>utf-8</project.reporting.outputencoding> <java.version>1.7</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactid> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>info.cukes</groupid> <artifactid>cucumber-java</artifactid> <version>${cucumber.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>info.cukes</groupid> <artifactid>cucumber-core</artifactid> <version>${cucumber.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>info.cukes</groupid> <artifactid>cucumber-spring</artifactid> <version>${cucumber.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>info.cukes</groupid> <artifactid>cucumber-junit</artifactid> <version>${cucumber.version}</version> <exclusions> <exclusion> <groupid>junit</groupid> <artifactid>junit</artifactid> </exclusion> </exclusions> </dependency> <dependency> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactid> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupid>org.springframework.boot</groupid> <artifactid>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactid> <configuration> <source>1.7</source> <target>1.7</target> </configuration> </plugin> <plugin> <groupid>org.codehaus.mojo</groupid> <artifactid>exec-maven-plugin</artifactid> <configuration> <source>1.7</source> <target>1.7</target> </configuration> <executions> <execution> <phase>integration-test</phase> <goals> <goal>java</goal> </goals> <configuration> <classpathscope>test</classpathscope> <mainclass>com.chhliu.test.cucumbertest.java</mainclass> <arguments> <argument>--plugin</argument> <argument>pretty</argument> <argument>--glue</argument> <argument>src/test/resources/</argument> </arguments> </configuration> </execution> </executions> </plugin> </plugins> </build> </project> |
2、编写service接口及其实现类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
package com.chhliu.service; /** * 模拟登录 * @author chhliu * */public interface userinfoservicei { boolean login(string username, string password, string confirmpassword); } |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
package com.chhliu.service; import org.springframework.stereotype.service; @service("userinfoservice") public class userinfoservice implements userinfoservicei{ public boolean login(string username, string password, string confirmpassword){ return (username.equals("chhliu") && password.equals("123456") && confirmpassword.equals("123456")); } } |
3、编写feature文件
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
#language: zh-cn #"zh-cn": { # "but": "*|但是<", # "and": "*|而且<|并且<|同时<", # "then": "*|那么<", # "when": "*|当<", # "name": "chinese simplified", # "native": "简体中文", # "feature": "功能", # "background": "背景", # "scenario": "场景|剧本", # "scenario_outline": "场景大纲|剧本大纲", # "examples": "例子", # "given": "*|假如<|假设<|假定<"# } @bank功能:假如我在银行取钱的时候,如果我登录成功并且输入的密码正确,那么会显示我的银行卡余额,假如余额为50万 场景:银行取钱 假如:我以"chhliu"登录 并且:输入的密码为"123456" 当:确认密码也为"123456"时 那么:显示银行卡余额为"500000" |
4、编写测试类
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
package com.chhliu.test; import org.junit.runner.runwith; import cucumber.api.cucumberoptions; import cucumber.api.junit.cucumber; /** * @runwith(cucumber.class) 这是一个运行器 ,指用cucumber来运行测试 * @cucumberoptions中的features,用于指定我们项目中要运行的feature的目录 * @cucumberoptions中的format,用于指定我们项目中要运行时生成的报告,并指定之后可以在target目录中找到对应的测试报告 * @cucumberoptions中的glue,用于指定项目运行时查找实现step定义文件的目录 * * 在实际项目中,随着项目的进行,一个测试工程可能由多个feature文件组成,并且每个feature文件中可能也是由多个scenario组成。默认情况下, * 每次运行是运行所有feature中的所有scenario。这样可能导致正常情况下运行一次测试脚本,需要非常长的时间来等待测试结果。 * 但是实际过程中,测试用例是有优先级等区分的。比如smoketest、regressiontest等。或者有时候会有特别小部分的用例,比如等级是critical, * 这些用例需要长时间运行来监测系统是否没有白页或者页面404等现象。 * 所以我们必须区分开所有的scenario,可以使我们在启动测试脚本时,可以根据我们需要来运行哪些模块的scenaro。这时我们可以使用tags * 在cucumber里tag是直接在feature、scenari或scenario outline关键字前给feature或scenario添加任意数量的前缀为@的tags,多个tag用空格来分隔 * @author chhliu * */@runwith(cucumber.class) @cucumberoptions(plugin = {"json:target/cucumber.json", "pretty"}, features = "src/test/resources") public class cucumbertest { } |
5、运行测试类,并对测试输出的未定义步骤进行完善
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
|
package com.chhliu.test; import javax.annotation.resource; import org.junit.assert; import com.chhliu.service.userinfoservicei; import cucumber.api.java.zh_cn.假如; import cucumber.api.java.zh_cn.当; import cucumber.api.java.zh_cn.那么; public class cucumber集成spring { @resource(name="userinfoservice") private userinfoservicei service; private string username; private string password; private string confirmpassword; @假如("^:我以\"([^\"]*)\"登录$") public void 我以_登录(string arg1) throws throwable { this.username = arg1; } @假如("^:输入的密码为\"([^\"]*)\"$") public void 输入的密码为(string arg1) throws throwable { this.password = arg1; } @当("^:确认密码也为\"([^\"]*)\"时$") public void 确认密码也为_时(string arg1) throws throwable { this.confirmpassword = arg1; } @那么("^:显示银行卡余额为\"([^\"]*)\"$") public void 显示银行卡余额为(string arg1) throws throwable { boolean islogin = service.login(username, password, confirmpassword); if(islogin){ system.out.println("登录成功!查询余额如下:"+arg1); assert.assertequals("500000", arg1); } } } |
6、在测试步骤上添加注解支持
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
@runwith(springjunit4classrunner.class) @contextconfiguration // 不加此注解,bean会注入不进去 @springboottest // 不加此注解会找不到bean public class cucumber集成spring{ } |
7、测试结果
2 scenarios (2 passed)
11 steps (11 passed)
0m0.091s
8、整合注意点
spring boot与cucumber整合的时候,有个地方需要注意,因为spring boot提倡去xml化,所以传统方式下,cucumber会读取classpath下的cucumber.xml配置文件来初始化bean的方式,和spring整合后,就不能用这种方式了,需要使用@contextconfiguration注解来实现类的加载,如果是需要加载配置文件的方式的话,可以如下使用:
|
1
|
@contextconfiguration(locations = { "classpath:applicationcontext.xml" }) |
如果使用注解的方式来整合的话,使用如下:
|
1
|
@contextconfiguration(classes=springbootcucumberapplication.class) |
或者直接
|
1
|
@contextconfiguration |
特别注意:@contextconfiguration注解必加,否则会出现bean注入失败
下面,我们从源码来看下为什么会造成这种情况。
该部分涉及的代码都在cucumber-spring包下的springfactory类中,重点我们看下下面这个类:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public void start() {// cucumber测试启动方法 if (stepclasswithspringcontext != null) {// 如果使用了@contextconfiguration注解的话,此处不为null testcontextmanager = new cucumbertestcontextmanager(stepclasswithspringcontext); } else {// 否则stepclasswithspringcontext就为null,会进入下面这个分支 if (beanfactory == null) { beanfactory = createfallbackcontext();// 这个方法是我们要跟的重点 } } notifycontextmanagerabouttestclassstarted(); if (beanfactory == null || isnewcontextcreated()) { beanfactory = testcontextmanager.getbeanfactory(); for (class<?> stepclass : stepclasses) { registerstepclassbeandefinition(beanfactory, stepclass); } } gluecodecontext.instance.start(); } |
我们在来跟下createfallbackcontext方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
private configurablelistablebeanfactory createfallbackcontext() { configurableapplicationcontext applicationcontext; if (getclass().getclassloader().getresource("cucumber.xml") != null) {// 会先根据classpath下的cucumber.xml来初始化<span style="font-family:arial, helvetica, sans-serif;">configurableapplicationcontext</span> applicationcontext = new classpathxmlapplicationcontext("cucumber.xml"); } else {// 如果没有配置cucumber.xml的话,会new genericapplicationcontext applicationcontext = new genericapplicationcontext(); } applicationcontext.registershutdownhook(); configurablelistablebeanfactory beanfactory = applicationcontext.getbeanfactory(); beanfactory.registerscope(gluecodescope.name, new gluecodescope()); for (class<?> stepclass : stepclasses) { registerstepclassbeandefinition(beanfactory, stepclass); } return beanfactory; } |
最后,来说下genericapplicationcontext这个类,该类会根据bean的type类型,然后newinstance实例,但是由于这个类中又注入了其他的类,而注入的类是无法通过new实例的方式来初始化的,所以最后就会注入失败,报空指针了。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/liuchuanhong1/article/details/77678620