实际项目场景:去除图片的纯白色背景图,获得一张透明底图片用于拼图功能
介绍两种途径的三种处理方式(不知道为啥想起了孔乙己),具体性能鶸并未对比,如果有大佬能告知,不胜感激。
core image core graphics/quarz 2d core image
core image是一个很强大的框架。它可以让你简单地应用各种滤镜来处理图像,比如修改鲜艳程度,色泽,或者曝光。 它利用gpu(或者cpu)来非常快速、甚至实时地处理图像数据和视频的帧。并且隐藏了底层图形处理的所有细节,通过提供的api就能简单的使用了,无须关心opengl或者opengl es是如何充分利用gpu的能力的,也不需要你知道gcd在其中发挥了怎样的作用,core image处理了全部的细节。

在苹果官方文档core image programming guide中,提到了chroma key filter recipe对于处理背景的范例
其中使用了hsv颜色模型,因为hsv模型,对于颜色范围的表示,相比rgb更加友好。
大致过程处理过程:
创建一个映射希望移除颜色值范围的立方体贴图cubemap,将目标颜色的alpha置为0.0f 使用cicolorcube滤镜和cubemap对源图像进行颜色处理获取到经过cicolorcube处理的core image对象ciimage,转换为core graphics中的cgimageref对象,通过imagewithcgimage:获取结果图片
注意:第三步中,不可以直接使用imagewithciimage:,因为得到的并不是一个标准的uiimage,如果直接拿来用,会出现不显示的情况。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
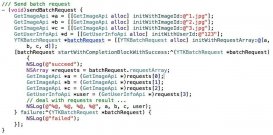
- (uiimage *)removecolorwithminhueangle:(float)minhueangle maxhueangle:(float)maxhueangle image:(uiimage *)originalimage{ ciimage *image = [ciimage imagewithcgimage:originalimage.cgimage]; cicontext *context = [cicontext contextwithoptions:nil];// kcicontextusesoftwarerenderer : cpurender /** 注意 * uiimage 通过ciimage初始化,得到的并不是一个通过类似cgimage的标准uiimage * 所以如果不用context进行渲染处理,是没办法正常显示的 */ ciimage *renderbgimage = [self outputimagewithoriginalciimage:image minhueangle:minhueangle maxhueangle:maxhueangle]; cgimageref renderimg = [context createcgimage:renderbgimage fromrect:image.extent]; uiimage *renderimage = [uiimage imagewithcgimage:renderimg]; return renderimage;}struct cubemap { int length; float dimension; float *data;};- (ciimage *)outputimagewithoriginalciimage:(ciimage *)originalimage minhueangle:(float)minhueangle maxhueangle:(float)maxhueangle{ struct cubemap map = createcubemap(minhueangle, maxhueangle); const unsigned int size = 64; // create memory with the cube data nsdata *data = [nsdata datawithbytesnocopy:map.data length:map.length freewhendone:yes]; cifilter *colorcube = [cifilter filterwithname:@"cicolorcube"]; [colorcube setvalue:@(size) forkey:@"inputcubedimension"]; // set data for cube [colorcube setvalue:data forkey:@"inputcubedata"]; [colorcube setvalue:originalimage forkey:kciinputimagekey]; ciimage *result = [colorcube valueforkey:kcioutputimagekey]; return result;}struct cubemap createcubemap(float minhueangle, float maxhueangle) { const unsigned int size = 64; struct cubemap map; map.length = size * size * size * sizeof (float) * 4; map.dimension = size; float *cubedata = (float *)malloc (map.length); float rgb[3], hsv[3], *c = cubedata; for (int z = 0; z < size; z++){ rgb[2] = ((double)z)/(size-1); // blue value for (int y = 0; y < size; y++){ rgb[1] = ((double)y)/(size-1); // green value for (int x = 0; x < size; x ++){ rgb[0] = ((double)x)/(size-1); // red value rgbtohsv(rgb,hsv); // use the hue value to determine which to make transparent // the minimum and maximum hue angle depends on // the color you want to remove float alpha = (hsv[0] > minhueangle && hsv[0] < maxhueangle) ? 0.0f: 1.0f; // calculate premultiplied alpha values for the cube c[0] = rgb[0] * alpha; c[1] = rgb[1] * alpha; c[2] = rgb[2] * alpha; c[3] = alpha; c += 4; // advance our pointer into memory for the next color value } } } map.data = cubedata; return map;} |
rgbtohsv在官方文档中并没有提及,笔者在下文中提到的大佬的博客中找到了相关转换处理。感谢
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
void rgbtohsv(float *rgb, float *hsv) { float min, max, delta; float r = rgb[0], g = rgb[1], b = rgb[2]; float *h = hsv, *s = hsv + 1, *v = hsv + 2; min = fmin(fmin(r, g), b ); max = fmax(fmax(r, g), b ); *v = max; delta = max - min; if( max != 0 ) *s = delta / max; else { *s = 0; *h = -1; return; } if( r == max ) *h = ( g - b ) / delta; else if( g == max ) *h = 2 + ( b - r ) / delta; else *h = 4 + ( r - g ) / delta; *h *= 60; if( *h < 0 ) *h += 360;} |
接下来我们试一下,去除绿色背景的效果如何

我们可以通过使用hsv工具,确定绿色hue值的大概范围为50-170
调用一下方法试一下
|
1
|
[[spimagechromafiltermanager sharedmanager] removecolorwithminhueangle:50 maxhueangle:170 image:[uiimage imagewithcontentsoffile:[[nsbundle mainbundle] pathforresource:@"nb" oftype:@"jpeg"]]] |
效果

效果还可以的样子。
如果认真观察hsv模型的同学也许会发现,我们通过指定色调角度(hue)的方式,对于指定灰白黑显得无能为力。我们不得不去用饱和度(saturation)和明度(value)去共同判断,感兴趣的同学可以在代码中判断alpha float alpha = (hsv[0] > minhueangle && hsv[0] < maxhueangle) ? 0.0f: 1.0f;那里试一下效果。(至于代码中为啥rgb和hsv这么转换,请百度他们的转换,因为鶸笔者也不懂。哎,鶸不聊生)
对于core image感兴趣的同学,请移步大佬的系列文章
ios8 core image in swift:自动改善图像以及内置滤镜的使用
ios8 core image in swift:更复杂的滤镜
ios8 core image in swift:人脸检测以及马赛克
ios8 core image in swift:视频实时滤镜
core graphics/quarz 2d
上文中提到的基于opengl的core image显然功能十分强大,作为视图另一基石的core graphics同样强大。对他的探究,让鶸笔者更多的了解到图片的相关知识。所以在此处总结,供日后查阅。
如果对探究不感兴趣的同学,请直接跳到文章最后 masking an image with color 部分
bitmap

在quarz 2d官方文档中,对于bitmap有如下描述:
a bitmap image (or sampled image) is an array of pixels (or samples). each pixel represents a single point in the image. jpeg, tiff, and png graphics files are examples of bitmap images.
|
1
|
32-bit and 16-bit pixel formats for cmyk and rgb color spaces in quartz 2d |
回到我们的需求,对于去除图片中的指定颜色,如果我们能够读取到每个像素上的rgba信息,分别判断他们的值,如果符合目标范围,我们将他的alpha值改为0,然后输出成新的图片,那么我们就实现了类似上文中cubemap的处理方式。
强大的quarz 2d为我们提供了实现这种操作的能力,下面请看代码示例:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
- (uiimage *)removecolorwithmaxr:(float)maxr minr:(float)minr maxg:(float)maxg ming:(float)ming maxb:(float)maxb minb:(float)minb image:(uiimage *)image{ // 分配内存 const int imagewidth = image.size.width; const int imageheight = image.size.height; size_t bytesperrow = imagewidth * 4; uint32_t* rgbimagebuf = (uint32_t*)malloc(bytesperrow * imageheight); // 创建context cgcolorspaceref colorspace = cgcolorspacecreatedevicergb();// 色彩范围的容器 cgcontextref context = cgbitmapcontextcreate(rgbimagebuf, imagewidth, imageheight, 8, bytesperrow, colorspace,kcgbitmapbyteorder32little | kcgimagealphanoneskiplast); cgcontextdrawimage(context, cgrectmake(0, 0, imagewidth, imageheight), image.cgimage); // 遍历像素 int pixelnum = imagewidth * imageheight; uint32_t* pcurptr = rgbimagebuf; for (int i = 0; i < pixelnum; i++, pcurptr++) { uint8_t* ptr = (uint8_t*)pcurptr; if (ptr[3] >= minr && ptr[3] <= maxr && ptr[2] >= ming && ptr[2] <= maxg && ptr[1] >= minb && ptr[1] <= maxb) { ptr[0] = 0; }else{ printf("\n---->ptr0:%d ptr1:%d ptr2:%d ptr3:%d<----\n",ptr[0],ptr[1],ptr[2],ptr[3]); } } // 将内存转成image cgdataproviderref dataprovider =cgdataprovidercreatewithdata(null, rgbimagebuf, bytesperrow * imageheight, nil); cgimageref imageref = cgimagecreate(imagewidth, imageheight,8, 32, bytesperrow, colorspace,kcgimagealphalast |kcgbitmapbyteorder32little, dataprovider,null,true,kcgrenderingintentdefault); cgdataproviderrelease(dataprovider); uiimage* resultuiimage = [uiimage imagewithcgimage:imageref]; // 释放 cgimagerelease(imageref); cgcontextrelease(context); cgcolorspacerelease(colorspace); return resultuiimage;} |
还记得我们在core image中提到的hsv模式的弊端吗?那么quarz 2d则是直接利用rgba的信息进行处理,很好的规避了对黑白色不友好的问题,我们只需要设置一下rgb的范围即可(因为黑白色在rgb颜色模式中,很好确定),我们可以大致封装一下。如下
|
1
2
3
|
- (uiimage *)removewhitecolorwithimage:(uiimage *)image{ return [self removecolorwithmaxr:255 minr:250 maxg:255 ming:240 maxb:255 minb:240 image:image];} |
|
1
2
3
|
- (uiimage *)removeblackcolorwithimage:(uiimage *)image{ return [self removecolorwithmaxr:15 minr:0 maxg:15 ming:0 maxb:15 minb:0 image:image];} |
看一下我们对于白色背景的处理效果对比

看起来似乎还不错,但是对于纱质的衣服,就显得很不友好。看一下笔者做的几组图片的测试

很显然,如果不是白色背景,“衣衫褴褛”的效果非常明显。这个问题,在笔者尝试的三种方法中,无一幸免,如果哪位大佬知道好的处理方法,而且能告诉鶸,将不胜感激。(先放俩膝盖在这儿)
除了上述问题外,这种对比每个像素的方法,读取出来的数值会同作图时出现误差。但是这种误差肉眼基本不可见。

如下图中,我们作图时,设置的rgb值分别为100/240/220 但是通过cg上述处理时,读取出来的值则为92/241/220。对比图中的“新的”“当前”,基本看不出色差。这点小问题各位知道就好,对实际去色效果影响并不大

masking an image with color
笔者尝试过理解并使用上一种方法后,在重读文档时发现了这个方法,简直就像是发现了father apple的恩赐。直接上代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
- (uiimage *)removecolorwithmaxr:(float)maxr minr:(float)minr maxg:(float)maxg ming:(float)ming maxb:(float)maxb minb:(float)minb image:(uiimage *)image{ const cgfloat mymaskingcolors[6] = {minr, maxr, ming, maxg, minb, maxb}; cgimageref ref = cgimagecreatewithmaskingcolors(image.cgimage, mymaskingcolors); return [uiimage imagewithcgimage:ref]; } |
总结
hsv颜色模式相对于rgb模式而言,更利于我们抠除图片中的彩色,而rgb则正好相反。笔者因为项目中,只需要去除白色背景,所以最终采用了最后一种方式。
原文链接:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000012523188