前言:
最近一直在致力于为公司app添加缓存功能,为了寻找一个最佳方案,这几天先做个技术预研,经过这两天的查找资料基本上确定了两个开源框架进行选择,这两个开源框架分别是:pincache、yycache,上篇已经简单介绍了pincache使用,本篇主要来学习一下yycache的使用方式,以及和pincache性能的简单对比。
关于yycache
1. 内存缓存(yymemorycache)
存储的单元是_yylinkedmapnode,除了key和value外,还存储了它的前后node的地址_prev,_next.整个实现基于_yylinkedmap,它是一个双向链表,除了存储了字典_dic外,还存储了头结点和尾节点.它实现的功能很简单,就是:有新数据了插入链表头部,访问过的数据结点移到头部,内存紧张时把尾部的结点移除.就这样实现了淘汰算法.因为内存访问速度很快,锁占用的时间少,所以用的速度最快的osspinlocklock
2. 硬盘缓存(yydiskcache)
采用的是文件和数据库相互配合的方式.有一个参数inlinethreshold,默认20kb,小于它存数据库,大于它存文件.能获得效率的提高.key:path,value:cache存储在nsmaptable里.根据path获得cache,进行一系列的set,get,remove操作更底层的是yykvstorage,它能直接对sqlite和文件系统进行读写.每次内存超过限制时,select key, filename, size from manifest order by last_access_time desc limit ?1会根据时间排序来删除最近不常用的数据.硬盘访问的时间比较长,如果用osspinlocklock锁会造成cpu消耗过大,所以用的dispatch_semaphore_wait来做.
yycache使用
1.同步方式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
//模拟数据nsstring *value=@"i want to know who is lcj ?";//模拟一个key//同步方式nsstring *key=@"key";yycache *yycache=[yycache cachewithname:@"lcjcache"];//根据key写入缓存value[yycache setobject:value forkey:key];//判断缓存是否存在bool iscontains=[yycache containsobjectforkey:key];nslog(@"containsobject : %@", iscontains?@"yes":@"no");//根据key读取数据id vuale=[yycache objectforkey:key];nslog(@"value : %@",vuale);//根据key移除缓存[yycache removeobjectforkey:key];//移除所有缓存[yycache removeallobjects]; |
2.异步方式
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
|
//模拟数据nsstring *value=@"i want to know who is lcj ?";//模拟一个key//异步方式nsstring *key=@"key";yycache *yycache=[yycache cachewithname:@"lcjcache"];//根据key写入缓存value[yycache setobject:value forkey:key withblock:^{ nslog(@"setobject sucess");}];//判断缓存是否存在[yycache containsobjectforkey:key withblock:^(nsstring * _nonnull key, bool contains) { nslog(@"containsobject : %@", contains?@"yes":@"no");}];//根据key读取数据[yycache objectforkey:key withblock:^(nsstring * _nonnull key, id<nscoding> _nonnull object) { nslog(@"objectforkey : %@",object);}];//根据key移除缓存[yycache removeobjectforkey:key withblock:^(nsstring * _nonnull key) { nslog(@"removeobjectforkey %@",key);}];//移除所有缓存[yycache removeallobjectswithblock:^{ nslog(@"removeallobjects sucess");}];//移除所有缓存带进度[yycache removeallobjectswithprogressblock:^(int removedcount, int totalcount) { nslog(@"removeallobjects removedcount :%d totalcount : %d",removedcount,totalcount);} endblock:^(bool error) { if(!error){ nslog(@"removeallobjects sucess"); }else{ nslog(@"removeallobjects error"); }}]; |
yycache缓存lru清理
lru(least recently used)算法大家都比较熟悉,翻译过来就是“最近最少使用”,lru缓存就是使用这种原理实现,简单的说就是缓存一定量的数据,当超过设定的阈值时就把一些过期的数据删除掉,比如我们缓存10000条数据,当数据小于10000时可以随意添加,当超过10000时就需要把新的数据添加进来,同时要把过期数据删除,以确保我们最大缓存10000条,那怎么确定删除哪条过期数据呢,采用lru算法实现的话就是将最老的数据删掉。接下来我们测试一下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
yycache *yycache=[yycache cachewithname:@"lcjcache"];[yycache.memorycache setcountlimit:50];//内存最大缓存数据个数[yycache.memorycache setcostlimit:1*1024];//内存最大缓存开销 目前这个毫无用处[yycache.diskcache setcostlimit:10*1024];//磁盘最大缓存开销[yycache.diskcache setcountlimit:50];//磁盘最大缓存数据个数[yycache.diskcache setautotriminterval:60];//设置磁盘lru动态清理频率 默认 60秒 |
模拟一下清理
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
|
for(int i=0 ;i<100;i++){ //模拟数据 nsstring *value=@"i want to know who is lcj ?"; //模拟一个key nsstring *key=[nsstring stringwithformat:@"key%d",i]; [yycache setobject:value forkey:key];}nslog(@"yycache.memorycache.totalcost:%lu",(unsigned long)yycache.memorycache.totalcost);nslog(@"yycache.memorycache.costlimit:%lu",(unsigned long)yycache.memorycache.costlimit);nslog(@"yycache.memorycache.totalcount:%lu",(unsigned long)yycache.memorycache.totalcount);nslog(@"yycache.memorycache.countlimit:%lu",(unsigned long)yycache.memorycache.countlimit);dispatch_after(dispatch_time(dispatch_time_now, (int64_t)(120 * nsec_per_sec)), dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{ nslog(@"yycache.diskcache.totalcost:%lu",(unsigned long)yycache.diskcache.totalcost); nslog(@"yycache.diskcache.costlimit:%lu",(unsigned long)yycache.diskcache.costlimit); nslog(@"yycache.diskcache.totalcount:%lu",(unsigned long)yycache.diskcache.totalcount); nslog(@"yycache.diskcache.countlimit:%lu",(unsigned long)yycache.diskcache.countlimit); for(int i=0 ;i<100;i++){ //模拟一个key nsstring *key=[nsstring stringwithformat:@"whoislcj%d",i]; id vuale=[yycache objectforkey:key]; nslog(@"key :%@ value : %@",key ,vuale); }}); |
yycache和pincache一样并没有实现基于最大内存开销进行lru,不过yycache实现了最大缓存数据个数进行lru清理,这一点也是选择yycache原因之一,对于yycache磁盘lru清理并不是及时清理,而是后台开启一个定时任务进行rlu清理操作,定时时间默认是60s。
yycache与pincache对比
对于我这里的使用场景大部分用于缓存json字符串,我这里就以存储字符串来对比一下写入与读取效率
1.写入性能对比
yycache
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
//模拟数据nsstring *value=@"i want to know who is lcj ?";//模拟一个keynsstring *key=@"key";//yycacheyycache *yycache=[yycache cachewithname:@"lcjcache"];//写入数据cfabsolutetime start = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent();[yycache setobject:value forkey:key withblock:^{ cfabsolutetime end = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent(); nslog(@" yycache async setobject time cost: %0.5f", end - start);}];cfabsolutetime start1 = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent();[yycache setobject:value forkey:key];cfabsolutetime end1 = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent();nslog(@" yycache sync setobject time cost: %0.5f", end1 - start1); |
运行结果

pincache
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
//pincache//模拟数据nsstring *value=@"i want to know who is lcj ?";//模拟一个keynsstring *key=@"key";pincache *pincache=[pincache sharedcache];//写入数据cfabsolutetime start = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent();[pincache setobject:value forkey:key block:^(pincache * _nonnull cache, nsstring * _nonnull key, id _nullable object) { cfabsolutetime end = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent(); nslog(@" pincache async setobject time cost: %0.5f", end - start);}];cfabsolutetime start1 = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent();[pincache setobject:value forkey:key];cfabsolutetime end1 = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent();nslog(@" pincache sync setobject time cost: %0.5f", end1 - start1); |
运行结果

通过上面的测试可以看出 同样大小的数据,无论同步方式还是异步方式,yycache性能都要由于pincache。
2.读取性能对比
yycache
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
yycache *yycache=[yycache cachewithname:@"lcjcache"];//模拟一个keynsstring *key=@"key";cfabsolutetime start = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent();//读取数据[yycache objectforkey:key withblock:^(nsstring * _nonnull key, id<nscoding> _nonnull object) { cfabsolutetime end = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent(); nslog(@" yycache async objectforkey time cost: %0.5f", end - start);}];cfabsolutetime start1 = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent();[yycache objectforkey:key];cfabsolutetime end1 = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent();nslog(@" yycache sync objectforkey time cost: %0.5f", end1 - start1); |
运行结果:

pincache
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
pincache *pincache=[pincache sharedcache]; //模拟一个key nsstring *key=@"key"; cfabsolutetime start = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent(); //读取数据 [pincache objectforkey:key block:^(pincache * _nonnull cache, nsstring * _nonnull key, id _nullable object) { cfabsolutetime end = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent(); nslog(@" pincache async objectforkey time cost: %0.5f", end - start); }] ; cfabsolutetime start1 = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent(); [pincache objectforkey:key]; cfabsolutetime end1 = cfabsolutetimegetcurrent(); nslog(@" pincache objectforkey time cost: %0.5f", end1 - start1); |
运行结果:
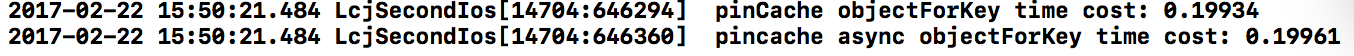
通过运行结果,在读取方面yycache也是优于pincache。
总结:
经过一番查阅资料和自己写例子测试,最终项目中决定使用yycache进行缓存管理。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/whoislcj/p/6429108.html