这是个常见的面试题,比如说通过二叉树的先序和中序遍历,得到二叉树的层序遍历等问题
先序+中序->建树
假设现在有个二叉树,如下:
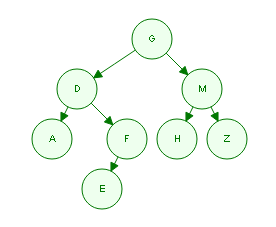
此时遍历顺序是:
|
1
2
3
|
PreOrder: GDAFEMHZ InOrder: ADEFGHMZ PostOrder: AEFDHZMG |
现在给出先序(preOrder)和中序(InOrder),建立一颗二叉树
或者给出中序(InOrder)和后序(PostOrder), 建立二叉树,其实是一样的
树节点的定义:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
class Tree{ char val; Tree left; Tree right; Tree(char val, Tree left, Tree right){ this.val = val; this.left = left; this.right = right; } Tree(){ } Tree(char val){ this.val = val; this.left = null; this.right =null; }} |
建树:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
public static Tree buildTree(char[] preOrder, char[] inOrder){ //preOrder是先序序列 //inOrder是中序序列 if(preOrder == null || preOrder.length == 0){ return null; } Tree root = new Tree(preOrder[0]); //找到inOrder中的root的位置 int inOrderIndex = 0; for (char i = 0; i < inOrder.length; i++){ if(inOrder[i] == root.val){ inOrderIndex = i; } } //preOrder的左子树和右子树部分 char[] preOrderLeft = Arrays.copyOfRange(preOrder, 1, 1+inOrderIndex); char[] preOrderRight = Arrays.copyOfRange(preOrder, 1+inOrderIndex, preOrder.length); //inOrder的左子树和右子树部分 char[] inOrderLeft = Arrays.copyOfRange(inOrder, 0, inOrderIndex); char[] inOrderRight = Arrays.copyOfRange(inOrder, inOrderIndex+1, inOrder.length); //递归建立左子树和右子树 Tree leftChild = buildTree(preOrderLeft, inOrderLeft); Tree rightChild = buildTree(preOrderRight, inOrderRight); root.left = leftChild; root.right = rightChild; return root;} |
中序+后序去建树其实是一样的,此处不写了
各种遍历
后序遍历
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public static void postOrderPrint(Tree root){ //后续遍历 //左右根 if(root.left != null){ postOrderPrint(root.left); } if(root.right != null){ postOrderPrint(root.right); } System.out.print(root.val + " "); } |
举一反三,先序和中序是一样的,此处不写了
层序遍历
可以用一个队列Queue,初始先把root节点加入到队列,当队列不为空的时候取队列头的节点node,打印node的节点值,如果node的左右孩子不为空将左右孩子加入到队列中即可
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
public static void layerOrderPrint(Tree root){ if(root == null){ return; } //层序遍历 Queue<Tree> qe = new LinkedList<Tree>(); qe.add(root); while(!qe.isEmpty()){ Tree node = qe.poll(); System.out.print(node.val + " "); if(node.left != null){ qe.add(node.left); } if(node.right != null){ qe.add(node.right); } } } |
深度优先和广度优先
其实就是换个说法而已,深度优先不就是先序遍历嘛,广度优先就是层序遍历
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
public static void deepFirstPrint(Tree root){ //深度优先遍历等价于先序遍历 //所以可以直接使用先序遍历 if(root == null){ return; } System.out.print(root.val + " "); if(root.left != null){ deepFirstPrint(root.left); } if(root.right != null){ deepFirstPrint(root.right); } }public static void deepFirstPrintNoneRec(Tree root){ //深度优先遍历的非递归形式 if(root == null){ return; } Stack<Tree> st = new Stack<Tree>(); st.add(root); while(!st.isEmpty()){ Tree node = st.pop(); System.out.print(node.val + " "); //栈是后进先出的 //先加右孩子后加左孩子 if(node.right != null){ st.add(node.right); } if(node.left != null){ st.add(node.left); } } } |
main函数:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public static void main(String[] args) { char[] preOrder = "GDAFEMHZ".toCharArray(); char[] inOrder = "ADEFGHMZ".toCharArray(); Tree root = Main.buildTree(preOrder, inOrder);// Main.postOrderPrint(root); //后序遍历// Main.layerOrderPrint(root); //层序遍历// Main.deepFirstPrint(root); //深度优先遍历// Main.deepFirstPrintNoneRec(root); //深度优先遍历的非递归版本 } |
总结
以上就是本文关于Java中二叉树的建立和各种遍历实例代码的全部内容,希望对大家有所帮助。如有不足之处,欢迎留言指出。感谢朋友们对本站的支持!
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/gavin__zhou/article/details/70199074















