本文实例讲述了java实现ArrayList根据存储对象排序功能。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下:
与c++中的qsort的实现极为相似,构建新的比较对象Comparator即可
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
|
package demo;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Collections;import java.util.Comparator;class Stu{ public int age; private String name; public Stu(String name,int age){ this.age=age; this.name=name; } public String toString(){ String str=name+"is "+age; return str; }}public class Sort{ @SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" }) public static void main(String[] args){ ArrayList<Stu> s=new ArrayList<Stu>(); s.add(new Stu("cjc",25)); s.add(new Stu("jake",17)); s.add(new Stu("john",30)); s.add(new Stu("Alice",23)); System.out.println("服务器之家测试结果:"); System.out.println("The order before sorting!"); System.out.println(s); //对集合中的元素更具年龄进行排序 Collections.sort(s,new Comparator(){ @Override public int compare(Object o1, Object o2) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Stu stu1=(Stu)o1; Stu stu2=(Stu)o2; return stu2.age-stu1.age; } }); System.out.println("The order after sorting!"); System.out.println(s); }} |
运行结果:
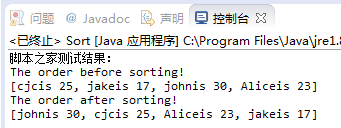
希望本文所述对大家java程序设计有所帮助。
原文链接:http://blog.csdn.net/cjc211322/article/details/41805079

















