使用spring boot + rabbitmq的时候,在开发过程中,可能会想要临时停用/启用监听,或修改监听消费者数量。如果每次修改都重启比较浪费时间,所以研究了一下不停机就启用停用监听或修改一些配置
一. 关于rabbitmq监听的配置
- 配置属性类:RabbitProperties,包含rabbitmq的认证、监听、发送者以及其他的一些配置
- 自动配置类:RabbitAutoConfiguration,主要配置rabbitmq的连接工厂和发送者等,不包含监听的配置
- rabbitmq监听的配置是RabbitAnnotationDrivenConfiguration,是通过RabbitAutoConfiguration引入的
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
@Configuration@ConditionalOnClass({ RabbitTemplate.class, Channel.class })@EnableConfigurationProperties(RabbitProperties.class)@Import(RabbitAnnotationDrivenConfiguration.class)public class RabbitAutoConfiguration { ...} |
RabbitAnnotationDrivenConfiguration中主要就是监听工厂的配置、监听工厂,但是这里也只是创建bean,并没有真正的初始化
通过配置里的bean类名,分析一下,rabbitmq的监听肯定是由监听工厂创建的,所以找到监听工厂SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
@Bean@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "rabbitListenerContainerFactory")public SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory rabbitListenerContainerFactory( SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactoryConfigurer configurer, ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) { SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory factory = new SimpleRabbitListenerContainerFactory(); configurer.configure(factory, connectionFactory); return factory;} |
既然自动配置里面没有初始化监听,那就应该是在其他地方调用的,进入监听工厂类中,发现有initializeContainer(SimpleMessageListenerContainer instance)方法,猜测初始化肯定与这个方法有关,所以查看有哪些地方调用,于是找到RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry.createListenerContainer(RabbitListenerEndpoint endpoint,RabbitListenerContainerFactory<?> factory)方法中有创建监听容器和初始化的代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
/** * Create and start a new {@link MessageListenerContainer} using the specified factory. * @param endpoint the endpoint to create a {@link MessageListenerContainer}. * @param factory the {@link RabbitListenerContainerFactory} to use. * @return the {@link MessageListenerContainer}. */protected MessageListenerContainer createListenerContainer(RabbitListenerEndpoint endpoint, RabbitListenerContainerFactory<?> factory) { MessageListenerContainer listenerContainer = factory.createListenerContainer(endpoint); if (listenerContainer instanceof InitializingBean) { try { ((InitializingBean) listenerContainer).afterPropertiesSet(); } catch (Exception ex) { throw new BeanInitializationException("Failed to initialize message listener container", ex); } } int containerPhase = listenerContainer.getPhase(); if (containerPhase < Integer.MAX_VALUE) { // a custom phase value if (this.phase < Integer.MAX_VALUE && this.phase != containerPhase) { throw new IllegalStateException("Encountered phase mismatch between container factory definitions: " + this.phase + " vs " + containerPhase); } this.phase = listenerContainer.getPhase(); } return listenerContainer;} |
继续找调用这个方法的地方,找到RabbitListenerEndpointRegistrar.afterPropertiesSet()方法之后,发现调用的地方很多了
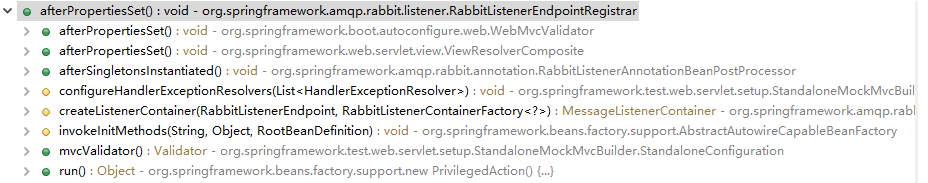
看看afterPropertiesSet方法,是InitializingBean接口中的,猜测应该是spring容器创建bean之后都会调用的bean初始化的方法,所以查找找到RabbitListenerEndpointRegistrar是在哪里创建的实例。原来是在RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor中的私有属性,而RabbitListenerAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是在RabbitBootstrapConfiguration这个自动配置里面初始化的,所以这就找到rabbitmq初始化监听的源头了
二. 动态管理rabbitmq监听
回到最初的问题,想要动态的启用停用mq的监听,所以先看看初始化配置的类,既然有初始化,那可能会有相关的管理,于是在RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry中找到了start()和stop()方法,里面有对监听容器进行操作,主要源码如下
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
/** * @return the managed {@link MessageListenerContainer} instance(s). */public Collection<MessageListenerContainer> getListenerContainers() { return Collections.unmodifiableCollection(this.listenerContainers.values());} @Overridepublic void start() { for (MessageListenerContainer listenerContainer : getListenerContainers()) { startIfNecessary(listenerContainer); }}/** * Start the specified {@link MessageListenerContainer} if it should be started * on startup or when start is called explicitly after startup. * @see MessageListenerContainer#isAutoStartup() */private void startIfNecessary(MessageListenerContainer listenerContainer) { if (this.contextRefreshed || listenerContainer.isAutoStartup()) { listenerContainer.start(); }}@Overridepublic void stop() { for (MessageListenerContainer listenerContainer : getListenerContainers()) { listenerContainer.stop(); }} |
写个controller,注入RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry,使用start()和stop()对监听进行启用停用的操作,并且RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry实例还可以获取监听容器,对监听的一些参数也能进行修改,比如消费者数量。代码如下:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
import java.util.Set;import javax.annotation.Resource;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.listener.RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry;import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.listener.SimpleMessageListenerContainer;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;import com.itopener.framework.ResultMap;/** * Created by fuwei.deng on 2017年7月24日. */@RestController@RequestMapping("rabbitmq/listener")public class RabbitMQController { @Resource private RabbitListenerEndpointRegistry rabbitListenerEndpointRegistry; @RequestMapping("stop") public ResultMap stop(){ rabbitListenerEndpointRegistry.stop(); return ResultMap.buildSuccess(); } @RequestMapping("start") public ResultMap start(){ rabbitListenerEndpointRegistry.start(); return ResultMap.buildSuccess(); } @RequestMapping("setup") public ResultMap setup(int consumer, int maxConsumer){ Set<String> containerIds = rabbitListenerEndpointRegistry.getListenerContainerIds(); SimpleMessageListenerContainer container = null; for(String id : containerIds){ container = (SimpleMessageListenerContainer) rabbitListenerEndpointRegistry.getListenerContainer(id); if(container != null){ container.setConcurrentConsumers(consumer); container.setMaxConcurrentConsumers(maxConsumer); } } return ResultMap.buildSuccess(); }} |
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://my.oschina.net/dengfuwei/blog/1595044

















