django提供了一个新的类来帮助你管理分页数据,这个类存放在django/core/paginator.py.它可以接收列表、元组或其它可迭代的对象。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
class paginator(object): def __init__(self, object_list, per_page, orphans=0, allow_empty_first_page=true): self.object_list = object_list self.per_page = int(per_page) self.orphans = int(orphans) self.allow_empty_first_page = allow_empty_first_page …… |
基本语法实例
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
#!/usr/bin/env python# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_ import os from django.core.paginator import paginatorobjects = ['john','paul','george','ringo','lucy','meiry','checy','wind','flow','rain']<br>p = paginator(objects,3) # 3条数据为一页,实例化分页对象print p.count # 10 对象总共10个元素print p.num_pages # 4 对象可分4页print p.page_range # xrange(1, 5) 对象页的可迭代范围 page1 = p.page(1) # 取对象的第一分页对象print page1.object_list # 第一分页对象的元素列表['john', 'paul', 'george']print page1.number # 第一分页对象的当前页值 1 page2 = p.page(2) # 取对象的第二分页对象print page2.object_list # 第二分页对象的元素列表 ['ringo', 'lucy', 'meiry']print page2.number # 第二分页对象的当前页码值 2 print page1.has_previous() # 第一分页对象是否有前一页 falseprint page1.has_other_pages() # 第一分页对象是否有其它页 true print page2.has_previous() # 第二分页对象是否有前一页 trueprint page2.has_next() # 第二分页对象是否有下一页 trueprint page2.next_page_number() # 第二分页对象下一页码的值 3print page2.previous_page_number() # 第二分页对象的上一页码值 1print page2.start_index() # 第二分页对象的元素开始索引 4print page2.end_index() # 第2分页对象的元素结束索引 6 |
官方解释在视图中的应用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
from django.core.paginator import paginator, emptypage, pagenotanintegerfrom django.shortcuts import render def listing(request): contact_list = contacts.objects.all() paginator = paginator(contact_list, 25) # show 25 contacts per page page = request.get.get('page') try: contacts = paginator.page(page) except pagenotaninteger: # if page is not an integer, deliver first page. contacts = paginator.page(1) except emptypage: # if page is out of range (e.g. 9999), deliver last page of results. contacts = paginator.page(paginator.num_pages) return render(request, 'list.html', {'contacts': contacts}) |
在template的html模板中的应用
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
{% for contact in contacts %} {# each "contact" is a contact model object. #} {{ contact.full_name|upper }}<br /> ...{% endfor %} <div class="pagination"> <span class="step-links"> {% if contacts.has_previous %} <a href="?page={{ contacts.previous_page_number }}">previous</a> {% endif %} <span class="current"> page {{ contacts.number }} of {{ contacts.paginator.num_pages }}. </span> {% if contacts.has_next %} <a href="?page={{ contacts.next_page_number }}">next</a> {% endif %} </span></div> |
举例讲述分页功能的使用目的说明
现要实现如下功能
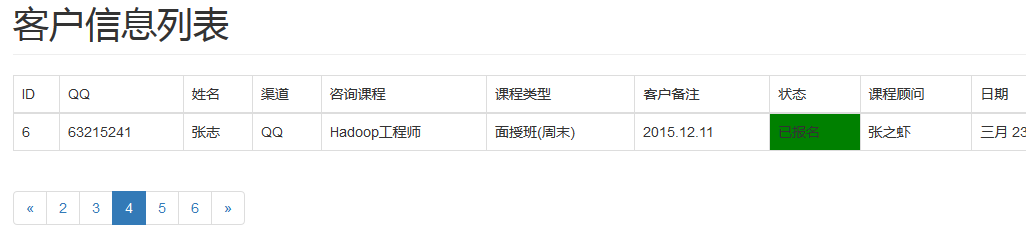
1、网页上显示分页数据,3条数据为一页
2、有分页导航功能,被选中页高亮显示
3、如果没有上一页或下一页,则不出现箭头导航
4、如果最后一页的数据少于2条,合并到上一页
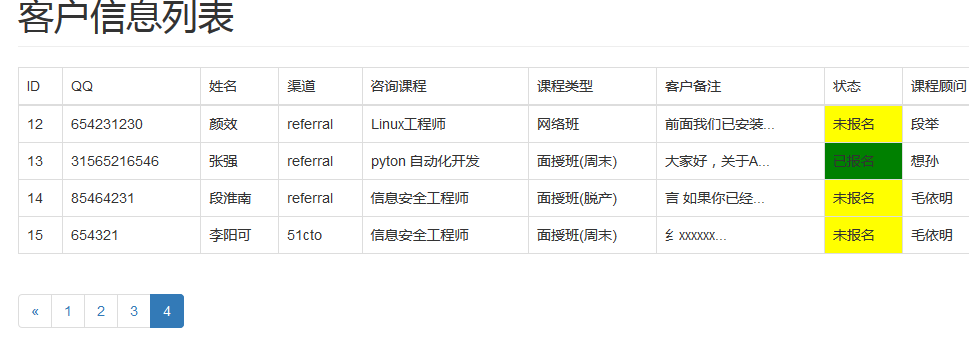
效果图
图1:
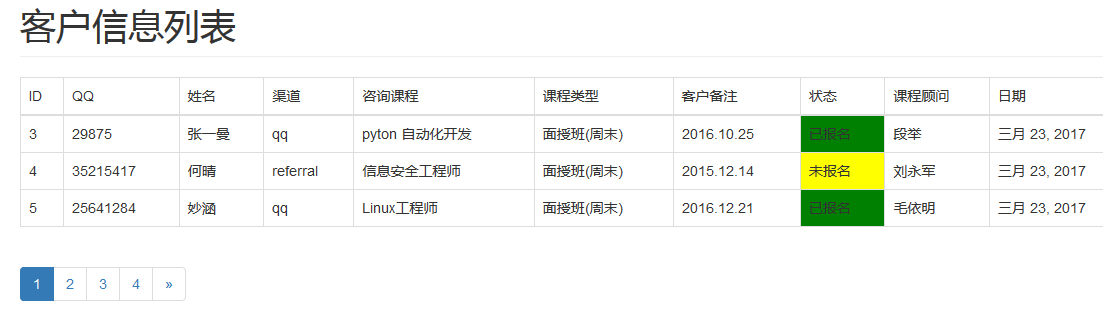
图2:
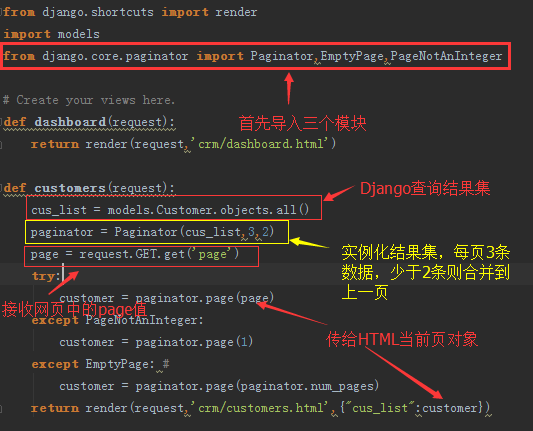
视图定义
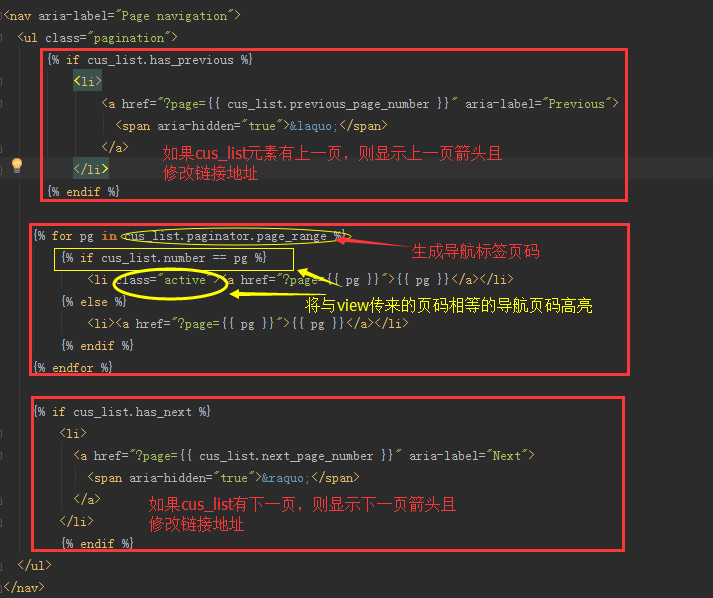
定义templates
分页功能优化
目标:
1、在template中的html模板中使用自定义函数
2、不管有多少分页,页面上最多显示5页
基础知识
django的模板语言包含了各种各样的内置标签和过滤器来满足你的应用需求,不过有时候你也会发现你的需要的功能不在内置的功能中,这时候你可以通过python语言自定义标签和过滤器来扩展模板引擎,然后在你的模板中使用{% load %}来加载使用它们。
在你的app下创建templatetags包,在其下创建python脚本来定义你的标签和过滤器,如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
polls/ __init__.py models.py templatetags/ __init__.py poll_extras.py views.py |
然后在你的模板中使用
|
1
|
{% load poll_extras %} |
项目实战
自定义过滤器和标签
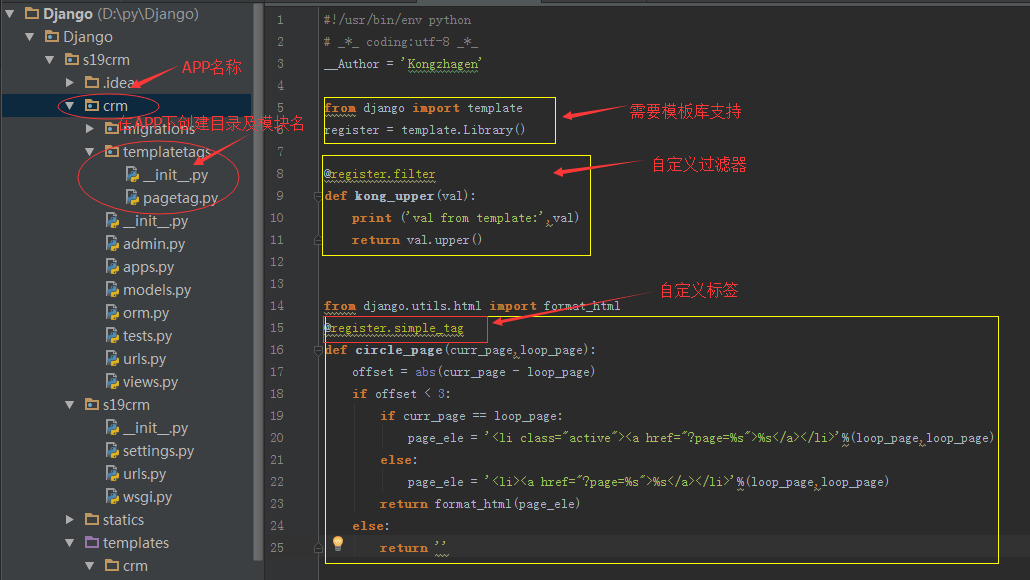
在模板中引用
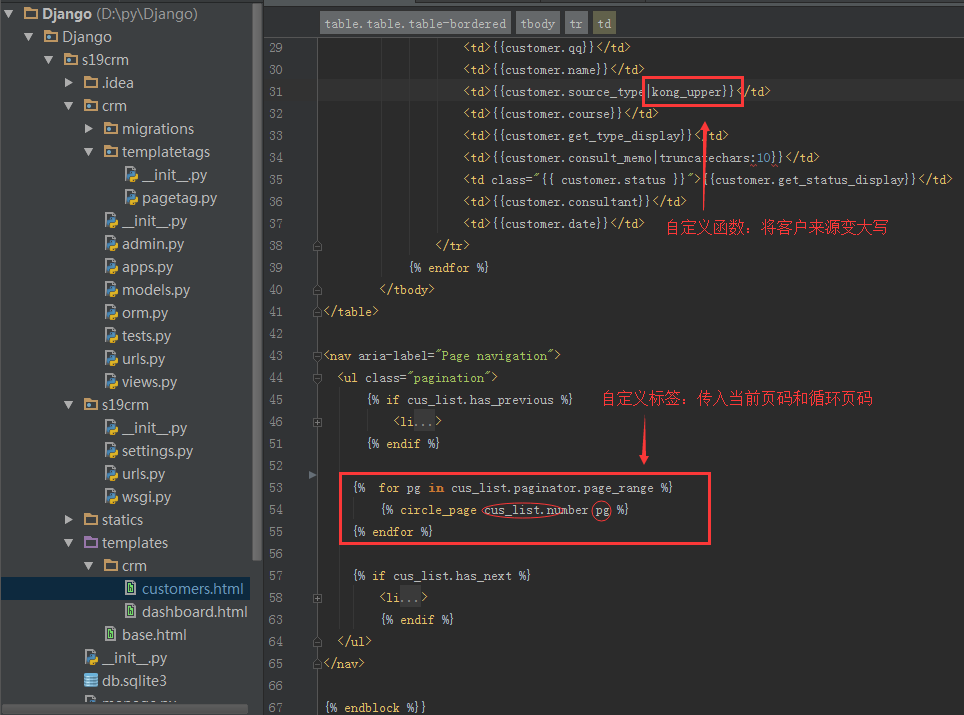
效果图:
https://github.com/kongzhagen/python/tree/master/django
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_37773766/article/details/80864658










