多列数据的读入以及处理
这次我们用到的数据是煤炭5500周价格的最高价和最低价。左侧为价格的数据表格,右侧为日期。

一、导入数据
这里我们就直接跳过讲解,如有不懂的,详见上一篇博客。见代码。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport replt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 设置字体plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 设置正负号# 导入数据,日期with open('日期.csv', encoding='gbk') as oo: day = oo.read()day_str = day.replace('\n', ',') # 换行替换成逗号day_list = re.split('[,]', day_str)list_days = []for s in range(len(day_list)-1): # 获得时间 list_days.append(day_list[s])# 将x转换成时间类型# 导入数据,金额with open('煤炭5500周价格波动数据.csv', encoding='gbk') as pp: sk = pp.read()ll = sk.replace('\n', ',') # 换行替换成逗号list_1 = re.split('[,]', ll) # 分割数据list_2 = []for s in range(len(list_1)-1): list_2.append(int(float(list_1[s]))) |
现在我们已经讲数据读取到相关的列表里,输出一下。
输出结果:
['2019/12/27', '2019/12/20', '2019/12/13', '2019/12/6', '2019/11/29', '2019/11/22', '2019/11/15', '2019/11/8', '2019/11/1', '2019/10/25', '2019/10/18', '2019/10/11', '2019/9/27', '2019/9/20', '2019/9/12', '2019/9/12', '2019/9/6', '2019/8/30', '2019/8/23', '2019/8/16', '2019/8/9', '2019/8/2', '2019/7/26', '2019/7/19', '2019/7/12', '2019/7/5', '2019/6/28', '2019/6/21', '2019/6/14', '2019/6/7', '2019/5/31', '2019/5/24', '2019/5/17', '2019/5/10', '2019/4/26', '2019/4/19', '2019/4/12', '2019/4/5', '2019/3/29', '2019/3/22', '2019/3/15', '2019/3/8', '2019/3/1', '2019/2/22', '2019/2/15', '2019/2/1', '2019/1/25', '2019/1/18', '2019/1/18', '2019/1/11', '2019/1/4', '2018/12/28']
[550, 555, 550, 555, 550, 555, 550, 555, 550, 555, 550, 555, 550, 555, 550, 555, 560, 565, 570, 575, 575, 580, 580, 585, 585, 590, 585, 590, 585, 590, 585, 590, 580, 585, 580, 585, 580, 590, 575, 585, 580, 590, 595, 600, 590, 600, 590, 595, 600, 605, 605, 615, 600, 610, 590, 600, 590, 600, 590, 600, 595, 600, 610, 620, 615, 620, 615, 620, 615, 625, 620, 625, 630, 640, 620, 630, 620, 625, 620, 630, 625, 630, 635, 645, 615, 625, 600, 605, 600, 605, 585, 590, 590, 595, 590, 595, 590, 595, 580, 590, 585, 595, 575, 580]
二、处理价格数据
我们可以看到0,2,4,6,8.......等偶数位的数值是周最低价,而单数位的数值是周最高价。我们可以用循环的方式读取到相关的数据。
代码如下。
这样就可以把数据进行分组了。以此类推,可以导入多列数据。
根据观察可以看到,时间列表是以降序的方式排列的,我们需要将数据转置过来,让列表数据改为升序。方法一、调整导入的CSV文件的数据顺序。方法二、我们引入reversed()函数。该函数有两种写法,作用主要是将列表,range(),字典里的数据进行逆向排列。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
逆转对象:list_x写法一、xxx = reversed(list_x)写法二、直接使用list(reversed(list_x)) |
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
aaa = reversed(list_average) 转置一个作为样例# 以上分割取得list_high,low,average# 设置x轴,y轴标签,设置表格标题plt.xlabel('时间')plt.ylabel('价格')plt.title('最高价/最低价/均价周期波动图')plt.legend(loc='upper right')plt.figure(figsize=(9, 8))输出图片大小900px*800px |
图表制作
需要的数据我们已经处理好了,接着就是生成图表。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport replt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 设置字体plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 设置正负号# 导入数据,日期with open('日期.csv', encoding='gbk') as oo: day = oo.read()day_str = day.replace('\n', ',') # 换行替换成逗号day_list = re.split('[,]', day_str)list_days = []for s in range(len(day_list)-1): # 获得时间 list_days.append(day_list[s])print(list_days)# 将x转换成时间类型# 导入数据,金额with open('煤炭5500周价格波动数据.csv', encoding='gbk') as pp: sk = pp.read()ll = sk.replace('\n', ',') # 换行替换成逗号list_1 = re.split('[,]', ll) # 分割数据list_2 = []for s in range(len(list_1)-1): list_2.append(int(float(list_1[s])))print(list_2)list_high = [] # 最高list_low = [] # 最低list_average = [] # 均值for k in range(len(list_2)): if k % 2 == 0: list_low.append(list_2[k]) list_average.append((list_2[k]+list_2[k+1])/2) else: list_high.append(list_2[k])aaa = reversed(list_average)# 以上分割取得list_high,low,average# 设置x轴,y轴标签,设置表格标题plt.xlabel('时间')plt.ylabel('价格')plt.title('最高价/最低价/均价周期波动图')# 设置标注 plt.figure(figsize=(9, 8)) # 制作折现图plt.plot(range(len(list_low)), list(reversed(list_high)), label='最高价', color='brown',marker='o',markerfacecolor='c',markersize='5')plt.plot(range(len(list_low)), list(reversed(list_low)), label='最低价', color='skyblue',marker='s',markerfacecolor='r',markersize='5')plt.plot(range(len(list_low)), list(reversed(list_average)), label='均价', color='lawngreen',marker='h',markerfacecolor='coral',markersize='5')# 设置标注plt.legend(loc='upper right') # 右上upper right 右下lower rightplt.show() |
这是到目前我们制作出来的折线图

替换x轴坐标点更改成日期
这里我们使用到plt.xticks()
|
1
2
3
4
|
书写格式:plt.xticks(被替换的数值(数据长的的列表),替换的数据,数据方向(默认横向))plt.xticks(range(len(list_low)), list(reversed(list_days)), rotation='vertical')vertical:数值方向,也可以写角度。 |
到这了我们就完成了全部的代码。
结束:最终代码
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport replt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 设置字体plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 设置正负号# 导入数据,日期with open('日期.csv', encoding='gbk') as oo: day = oo.read()day_str = day.replace('\n', ',') # 换行替换成逗号day_list = re.split('[,]', day_str)list_days = []for s in range(len(day_list)-1): # 获得时间 list_days.append(day_list[s])print(list_days)# 将x转换成时间类型# 导入数据,金额with open('煤炭5500周价格波动数据.csv', encoding='gbk') as pp: sk = pp.read()ll = sk.replace('\n', ',') # 换行替换成逗号list_1 = re.split('[,]', ll) # 分割数据list_2 = []for s in range(len(list_1)-1): list_2.append(int(float(list_1[s])))print(list_2)list_high = [] # 最高list_low = [] # 最低list_average = [] # 均值for k in range(len(list_2)): if k % 2 == 0: list_low.append(list_2[k]) list_average.append((list_2[k]+list_2[k+1])/2) else: list_high.append(list_2[k])aaa = reversed(list_average)# 以上分割取得list_high,low,average# 设置x轴,y轴标签,设置表格标题plt.xlabel('时间')plt.ylabel('价格')plt.title('最高价/最低价/均价周期波动图')# 设置标注 plt.figure(figsize=(9, 8)) plt.xticks(range(len(list_low)), list(reversed(list_days)), rotation='vertical')# 设置折现图plt.plot(range(len(list_low)), list(reversed(list_high)), label='最高价', color='brown',marker='o',markerfacecolor='c',markersize='5')plt.plot(range(len(list_low)), list(reversed(list_low)), label='最低价', color='skyblue',marker='s',markerfacecolor='r',markersize='5')plt.plot(range(len(list_low)), list(reversed(list_average)), label='均价', color='lawngreen',marker='h',markerfacecolor='coral',markersize='5')# 设置标注plt.legend(loc='upper right') plt.show() |
结果示意图:
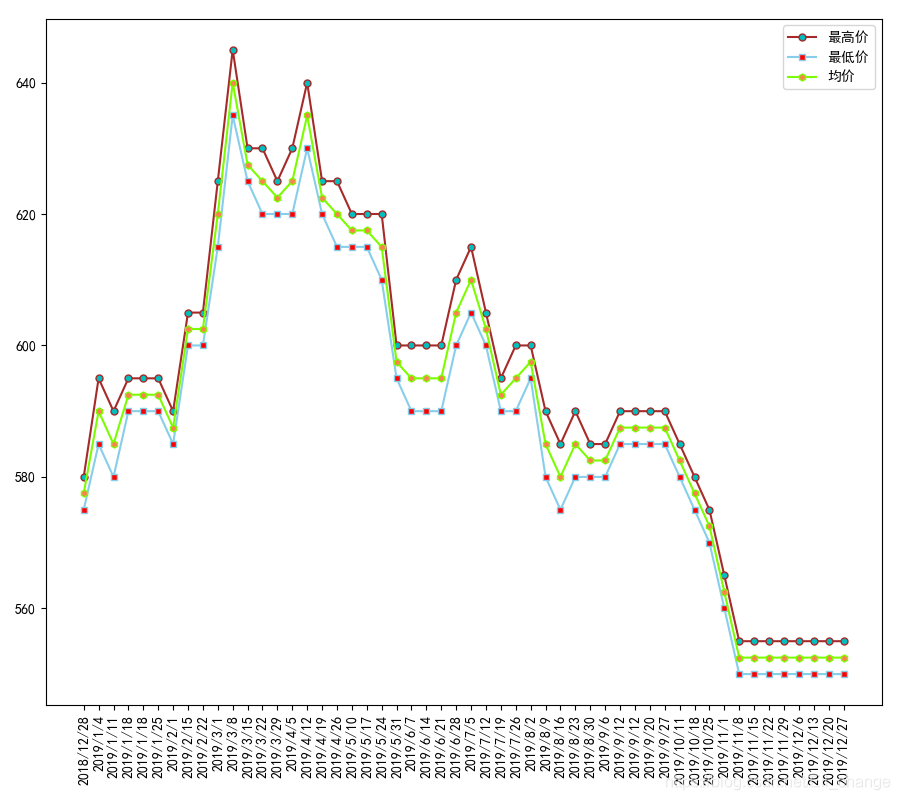
总结
到此这篇关于Python读取多列数据以及用matplotlib制作图片的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python读取多列数据用matplotlib制作图片内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Eli_change/article/details/108685669










