在网上的一些资料的基础上自己又添了些新内容,算是Python socket编程练手吧。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
|
#coding=utf-8import socketimport timeimport sysimport structimport threadingfrom threading import Thread,activeCountresults=[]def portScanner(ip,port): server = (ip,port) sockfd = socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM) sockfd.settimeout(0.1) #设置阻塞模式下socket的超时时间 ret = sockfd.connect_ex(server) #成功返回0,失败返回error的值。 if not ret: sockfd.close() results.append([ip,port]) #print '%s:%s is opened...' % (ip,port) else: sockfd.close() pass return '' def ip2num(ip): #将ip地址转换成数字 lp = [int(x) for x in ip.split('.')] return lp[0] << 24 | lp[1] << 16 | lp[2] << 8 |lp[3]def num2ip(num): ip = ['','','',''] ip[3] = (num & 0xff) ip[2] = (num & 0xff00) >> 8 ip[1] = (num & 0xff0000) >> 16 ip[0] = (num & 0xff000000) >> 24 return '%s.%s.%s.%s' % (ip[0],ip[1],ip[2],ip[3])def iprange(ip1,ip2): num1 =socket.ntohl(struct.unpack("I",socket.inet_aton(str(ip1)))[0]) num2 =socket.ntohl(struct.unpack("I",socket.inet_aton(str(ip2)))[0]) tmp = num2 - num1 if tmp < 0: return None else: return num1,num2,tmpif __name__ == '__main__': if((len(sys.argv)!= 4)&(len(sys.argv)!= 2)): #用法说明 print 'Usage:\n\tscanner.py startip endip port' print '\tscanner.py ip' sys.exit() if len(sys.argv)==4: #对某一IP段的扫描 time_start=time.time() #起始时间 startip = sys.argv[1] #起始IP endip = sys.argv[2] #结束IP port = int(sys.argv[3]) #端口号 res = iprange(startip,endip) if not res: print 'endip must be bigger than startone' sys.exit() elif res[2] == 0: portScanner(startip,port) else: for x in xrange(int(res[2])+1): #IP地址依次递增 startipnum = ip2num(startip) startipnum = startipnum + x if activeCount() <=1000: Thread(target=portScanner,args=(num2ip(startipnum),port)).start() print "There are %d hosts." %len(results) results.sort() for ip,port in results: print "%s:%d is opened..." %(ip,port) times=time.time()-time_start #用时 print 'use time : %s' % times if len(sys.argv)==2: time_start=time.time() port=0 ip=sys.argv[1] while(port<2000): if activeCount() <= 40: #设置40线程扫描 Thread(target = portScanner, args = (ip, port)).start() port=port+1 results.sort() for ip,port in results: print "%s:%d is opened..." %(ip,port) times=time.time()-time_start print 'use time : %s' % times |
使用效果如下:
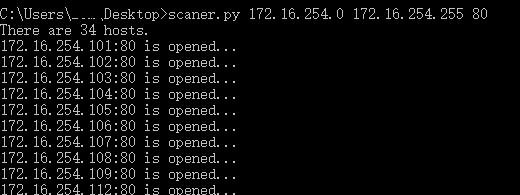
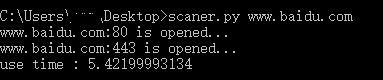
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/lovealways/p/6550218.html










