前言
前面几篇文章,学习了Spring IOC、Bean实例化过程、AOP、事务的源码和设计思想,了解了Spring的整体运行流程,但如果是web开发,那么必不可少的还有Spring MVC,本篇主要分析在请求调用过程中SpringMVC的实现原理,通过本篇要搞懂它是怎么解决请求、参数、返回值映射等问题的。
正文
请求入口
我们都知道前端调用后端接口时,都会通过Servlet进行转发,而Servlet的声明周期包含下面四个阶段:
实例化(new)
初始化(init)
执行(service调用doGet/doPost)
销毁(destroy)
前两个阶段在Spring启动阶段就做好了(init根据配置可能是第一次请求时才会调用),销毁是服务关闭的时候进行,本文主要分析的就是请求执行阶段。我们知道SpringMVC的核心就是DispatcherServlet,该类是对Servlet的扩展,所以直接从该类的service方法开始,但在此类中没有service方法,那肯定是在其父类中,我们先来看看其继承体系:
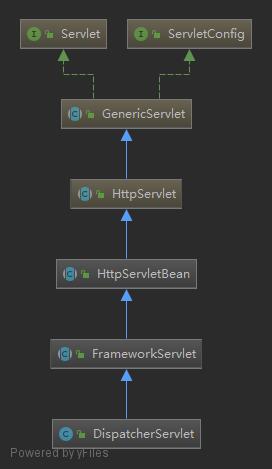
逐个往上找,在FrameworkServlet方法中就有一个service方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
|
protected void service(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)throws ServletException, IOException {HttpMethod httpMethod = HttpMethod.resolve(request.getMethod());if (httpMethod == HttpMethod.PATCH || httpMethod == null) {processRequest(request, response);}else {super.service(request, response);}}protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException{ String method = req.getMethod(); if (method.equals(METHOD_GET)) { long lastModified = getLastModified(req); if (lastModified == -1) { doGet(req, resp); } else { long ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader(HEADER_IFMODSINCE); if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified) { maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); doGet(req, resp); } else { resp.setStatus(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_MODIFIED); } } } else if (method.equals(METHOD_HEAD)) { long lastModified = getLastModified(req); maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); doHead(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_POST)) { doPost(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_PUT)) { doPut(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_DELETE)) { doDelete(req, resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_OPTIONS)) { doOptions(req,resp); } else if (method.equals(METHOD_TRACE)) { doTrace(req,resp); } else { String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); Object[] errArgs = new Object[1]; errArgs[0] = method; errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); resp.sendError(HttpServletResponse.SC_NOT_IMPLEMENTED, errMsg); }} |
但其主要还是调用父类HttpServlet中的方法,而该类又会根据不同的请求方式会调到子类中,最后的核心方法就是DispatcherServlet中的doDispatch方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
|
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; //异步管理 WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { //文件上传 processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); //这个方法很重要,重点看 // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest); if (mappedHandler == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } //获取跟HandlerMethod匹配的HandlerAdapter对象 // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler()); // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } //前置过滤器,如果为false则直接返回 if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } //调用到Controller具体方法,核心方法调用,重点看看 // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); //中置过滤器 mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); } catch (Exception ex) { dispatchException = ex; } catch (Throwable err) { // As of 4.3, we're processing Errors thrown from handler methods as well, // making them available for @ExceptionHandler methods and other scenarios. dispatchException = new NestedServletException("Handler dispatch failed", err); } //视图渲染及后置过滤器执行 processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); } catch (Exception ex) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, ex); } catch (Throwable err) { triggerAfterCompletion(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, new NestedServletException("Handler processing failed", err)); } finally { if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Instead of postHandle and afterCompletion if (mappedHandler != null) { mappedHandler.applyAfterConcurrentHandlingStarted(processedRequest, response); } } else { // Clean up any resources used by a multipart request. if (multipartRequestParsed) { cleanupMultipart(processedRequest); } } } } |
MVC的所有处理逻辑都在这个方法中,先总结一下这个方法的实现逻辑,首先根据请求的url拿到缓存中的HandlerMethod对象和执行链对象,HandlerMethod中封装了controller对象、方法对象和方法参数等信息,执行链则是包含了一个个HandlerInterceptor拦截器;然后再通过HandlerMethod拿到对应的HandlerAdapter,这个对象的作用就是去适配我们的controller;准备工作做完后,首先会执行前置过滤,如果被拦截则直接返回,否则就去调用controller中的方法执行我们的业务逻辑并返回一个ModelView对象;接着执行中置过滤器,以及处理全局异常捕获器捕获到异常;最后进行视图渲染返回并执行后置过滤器进行资源释放等工作。
以上就是MVC的整体执行流程,下面就逐个来分析,首先进入getHandler方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {//handlerMappering实例if (this.handlerMappings != null) {for (HandlerMapping mapping : this.handlerMappings) {//获取HandlerMethod和过滤器链的包装类HandlerExecutionChain handler = mapping.getHandler(request);if (handler != null) { return handler;}}}return null;} |
是委托给HandlerMapping对象的,这是一个接口,主要的实现类是RequestMappingHandlerMapping,同样先来看看其继承体系:
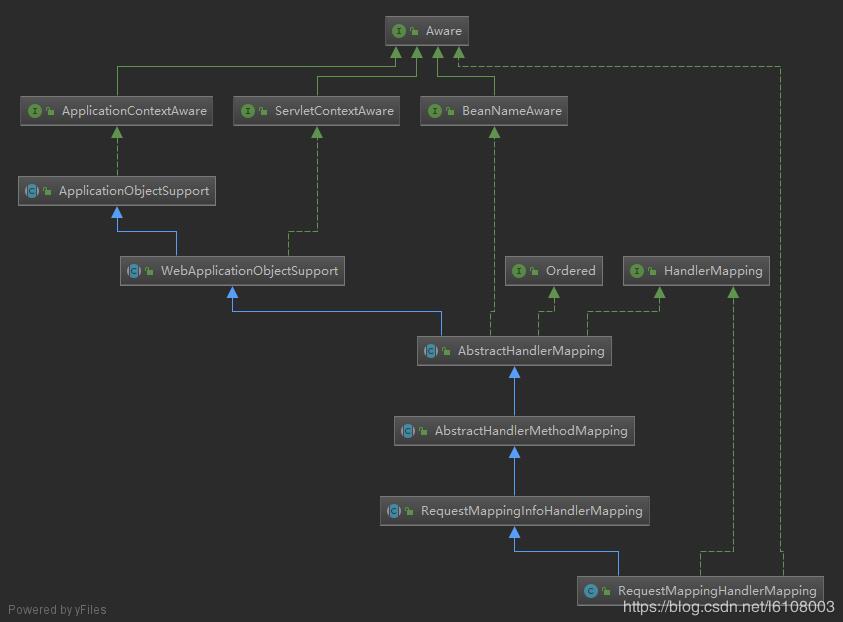
这个类是管理请求和处理类之间的映射关系的,你是否疑惑它是在哪里实例化的呢?下面先来看看MVC组件的初始化。
组件初始化
这里我以自动化配置的注解方式说明,Spring提供了一个@EnableWebMvc,通过前面的学习我们知道在这个注解中必定导入了一个配置类,点进去可以看到是DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration,这个类就是负责MVC的组件和扩展实现的初始化,其本身我们先不看,先看其父类WebMvcConfigurationSupport,这个类我们应该不陌生,要做一些自定义扩展时就需要继承该类(如拦截器Interceptor),同样作用的类还有WebMvcConfigurerAdapter,这个类是对前者相对安全的扩展,为什么是相对安全呢?因为继承前者会导致自动配置失效,而使用后者则不必担心此问题,只需要在类上加上@EnableWebMvc注解。
在WebMvcConfigurationSupport中我们可以看到很多@Bean标注的方法,也就是mvc组件的实例化,这里主要看看requestMappingHandlerMapping,其余的可自行阅读理解,也就是一些Bean的注册:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public RequestMappingHandlerMapping requestMappingHandlerMapping() {RequestMappingHandlerMapping mapping = createRequestMappingHandlerMapping();mapping.setOrder(0);mapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors());mapping.setContentNegotiationManager(mvcContentNegotiationManager());mapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());......省略return mapping;} |
这里主要看getInterceptors方法如何获取拦截器的:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
protected final Object[] getInterceptors() {if (this.interceptors == null) {InterceptorRegistry registry = new InterceptorRegistry();//钩子方法,需要自己定义addInterceptors(registry);registry.addInterceptor(new ConversionServiceExposingInterceptor(mvcConversionService()));registry.addInterceptor(new ResourceUrlProviderExposingInterceptor(mvcResourceUrlProvider()));this.interceptors = registry.getInterceptors();}return this.interceptors.toArray();} |
第一次进来会调用addInterceptors添加拦截器,这是一个模板方法,在子类DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration中实现:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
private final WebMvcConfigurerComposite configurers = new WebMvcConfigurerComposite();protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {this.configurers.addInterceptors(registry);}public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {for (WebMvcConfigurer delegate : this.delegates) {delegate.addInterceptors(registry);}} |
可以看到最终是调用WebMvcConfigurer的addInterceptors方法,也就是我们对WebMvcConfigurerAdapter的自定义扩展。看到这里我们应该明白了MVC的组件是如何添加到IOC容器中的,但是DispatcherServlet又是怎么获取到它们的呢?回到之前的代码中,在DispatcherServlet这个类中有一个onRefresh方法,这个方法又调用了initStrategies方法完成了MVC九大组件的注册:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
protected void onRefresh(ApplicationContext context) {initStrategies(context);}protected void initStrategies(ApplicationContext context) {initMultipartResolver(context);initLocaleResolver(context);initThemeResolver(context);initHandlerMappings(context);initHandlerAdapters(context);initHandlerExceptionResolvers(context);initRequestToViewNameTranslator(context);initViewResolvers(context);initFlashMapManager(context);}private void initHandlerMappings(ApplicationContext context) {this.handlerMappings = null;if (this.detectAllHandlerMappings) {// Find all HandlerMappings in the ApplicationContext, including ancestor contexts.Map<String, HandlerMapping> matchingBeans = BeanFactoryUtils.beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(context, HandlerMapping.class, true, false);if (!matchingBeans.isEmpty()) {this.handlerMappings = new ArrayList<>(matchingBeans.values());// We keep HandlerMappings in sorted order.AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(this.handlerMappings);}}else {try {HandlerMapping hm = context.getBean(HANDLER_MAPPING_BEAN_NAME, HandlerMapping.class);this.handlerMappings = Collections.singletonList(hm);}catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {// Ignore, we'll add a default HandlerMapping later.}}if (this.handlerMappings == null) {this.handlerMappings = getDefaultStrategies(context, HandlerMapping.class);}} |
以initHandlerMappings为例,其它组件实现逻辑基本一样。首先从IOC容器中拿到handlerMappings的所有实现类(WebMvcConfigurationSupport中注入的对象就在这里被获取到),若没有,则从DispatcherServlet.properties配置文件中(这个配置在spring-webmvc工程下org/springframework/web/servlet/DispatcherServlet.properties)获取默认的配置:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
org.springframework.web.servlet.LocaleResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.AcceptHeaderLocaleResolverorg.springframework.web.servlet.ThemeResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.theme.FixedThemeResolverorg.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerMapping=org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.BeanNameUrlHandlerMapping,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMappingorg.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerAdapter=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.HttpRequestHandlerAdapter,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapterorg.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.ResponseStatusExceptionResolver,\ org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.support.DefaultHandlerExceptionResolverorg.springframework.web.servlet.RequestToViewNameTranslator=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.DefaultRequestToViewNameTranslatororg.springframework.web.servlet.ViewResolver=org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolverorg.springframework.web.servlet.FlashMapManager=org.springframework.web.servlet.support.SessionFlashMapManager |
但是onRefresh又是在什么时候调用的呢?有两个地方,一个是Servlet初始化时会调用到initWebApplicationContext进行容器的初始化,这个方法中就会触发onRefresh;另外还有一个,在FrameworkServlet中有一个onApplicationEvent方法,而这个方法又会被内部类ContextRefreshListener调用,这个类实现了ApplicationListener接口,表示会接收容器刷新事件。
以上就就是MVC HandlerMapping组件的初始化逻辑,其它组件实现逻辑相同,下面不再分析。
调用Controller
回到getHandler方法,其调用的是AbstractHandlerMapping类的方法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {//根据请求的uri拿到对应的HandlerMethod对象Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);if (handler == null) {handler = getDefaultHandler();}if (handler == null) {return null;}// Bean name or resolved handler?if (handler instanceof String) {String handlerName = (String) handler;handler = obtainApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName);}//获取HandlerMethod和过滤器链的包装类HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Mapped to " + handler);}else if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && !request.getDispatcherType().equals(DispatcherType.ASYNC)) {logger.debug("Mapped to " + executionChain.getHandler());}//是否是跨域请求,就是查看request请求头中是否有Origin属性if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) {//自定义的钩子方法获取跨域配置CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigurationSource.getCorsConfiguration(request);//注解获取跨域配置CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request);CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig);//这里设置了跨域的过滤器CorsInterceptorexecutionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config);}return executionChain;} |
先看AbstractHandlerMethodMapping.getHandlerInternal:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
|
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {//从request对象中获取uri,/common/query2String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request);this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock();try {//根据uri从映射关系中找到对应的HandlerMethod对象HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);//把Controller类实例化return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null);}finally {this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock();}}protected HandlerMethod lookupHandlerMethod(String lookupPath, HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception {List<Match> matches = new ArrayList<>();// 根据url拿到对应的RequestMappingInfoList<T> directPathMatches = this.mappingRegistry.getMappingsByUrl(lookupPath);if (directPathMatches != null) {addMatchingMappings(directPathMatches, matches, request);}if (matches.isEmpty()) {// No choice but to go through all mappings...addMatchingMappings(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), matches, request);}if (!matches.isEmpty()) {Comparator<Match> comparator = new MatchComparator(getMappingComparator(request));matches.sort(comparator);Match bestMatch = matches.get(0);if (matches.size() > 1) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace(matches.size() + " matching mappings: " + matches);}if (CorsUtils.isPreFlightRequest(request)) { return PREFLIGHT_AMBIGUOUS_MATCH;}Match secondBestMatch = matches.get(1);//如果两个RequestMappinginfo什么都相同,报错if (comparator.compare(bestMatch, secondBestMatch) == 0) { Method m1 = bestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); Method m2 = secondBestMatch.handlerMethod.getMethod(); String uri = request.getRequestURI(); throw new IllegalStateException( "Ambiguous handler methods mapped for '" + uri + "': {" + m1 + ", " + m2 + "}");}}request.setAttribute(BEST_MATCHING_HANDLER_ATTRIBUTE, bestMatch.handlerMethod);handleMatch(bestMatch.mapping, lookupPath, request);return bestMatch.handlerMethod;}else {return handleNoMatch(this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().keySet(), lookupPath, request);}}private void addMatchingMappings(Collection<T> mappings, List<Match> matches, HttpServletRequest request) {for (T mapping : mappings) {// 拿到匹配的RequestMappingInfo对象,有可能url相同,@RequestMapping的属性(请求方式、参数等)匹配不上T match = getMatchingMapping(mapping, request);if (match != null) {//RequestMappingInfo对象和HandlerMethod对象封装到Match对象中,其实就是注解属性和Method对象的映射matches.add(new Match(match, this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping)));}}} |
这里逻辑很简单,就是通过请求url从urlLookup中拿到对应的RequestMappingInfo(每一个 @RequestMapping对应一个RequestMappingInfo对象)对象,再根据RequestMappingInfo对象从mappingLookup拿到对应的HandlerMethod并返回。
但这里你可能会比较好奇urlLookup和mappingLookup从哪里来的,仔细观察你会发现当前这个类实现了一个接口InitializingBean,实现了这个接口的类会在该类的Bean实例化完成后调用afterPropertiesSet方法,上面的映射关系就是在这个方法中做的。实际上这个方法不止完成了上面两个映射关系,还有下面两个:
corsLookup:handlerMethod -> corsConfig
registry:RequestMappingInfo -> MappingRegistration(包含url、handlerMethod、RequestMappingInfo、name等信息)
这里就不展开分析了,奉上一张时序图,读者可根据下面的时序图自行分析:
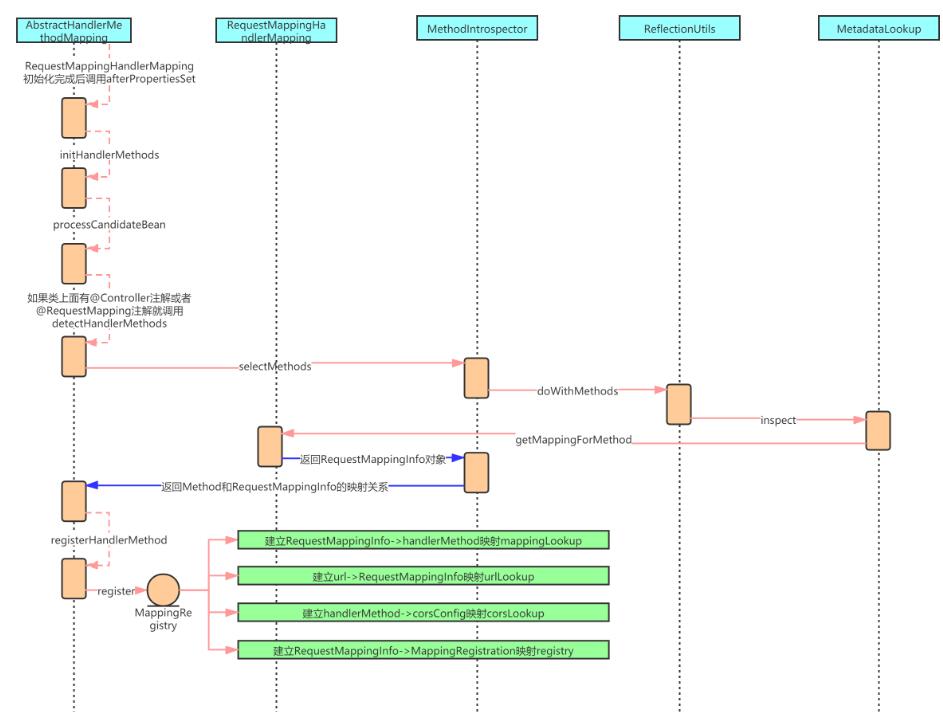
拿到HandlerMethod对象后,又会通过getHandlerExecutionChain方法去获取到所有的HandlerInterceptor拦截器对象,并连同HandlerMethod对象一起封装为HandlerExecutionChain。之后是获取跨域配置,这里不详细分析。
拿到HandlerExecutionChain对象后返回到doDispatch方法,又调用了getHandlerAdapter
方法拿到HandlerAdapter:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException {//根据handlerMethod对象,找到合适的HandlerAdapter对象,这里用到了策略模式if (this.handlerAdapters != null) {for (HandlerAdapter adapter : this.handlerAdapters) {if (adapter.supports(handler)) { return adapter;}}}} |
这里的handlerAdapters变量值从哪里来?相信不用我再分析,主要看这里的设计思想,典型的策略模式。
之后调用完前置过滤器后,才是真正调用我们controller方法的逻辑,通过HandlerAdapter.handle去调用,最终会调用到ServletInvocableHandlerMethod.invokeAndHandle:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {//具体调用逻辑,重点看Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);setResponseStatus(webRequest);if (returnValue == null) {if (isRequestNotModified(webRequest) || getResponseStatus() != null || mavContainer.isRequestHandled()) {mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);return;}}else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) {mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true);return;}mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false);Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers");try {//返回值处理this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue( returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest);}catch (Exception ex) {if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace(formatErrorForReturnValue(returnValue), ex);}throw ex;}} |
这个方法里面主要看invokeForRequest和handleReturnValue的调用,前者是完成参数绑定并调用controller,后者则是对返回值进行处理并封装到ModelAndViewContainer中。先来看invokeForRequest:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {//获取参数数组Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {logger.trace("Arguments: " + Arrays.toString(args));}return doInvoke(args);} |
doInvoke就是完成反射调用,主要还是看参数绑定的实现逻辑,在getMethodArgumentValues方法中:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
|
protected Object[] getMethodArgumentValues(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {if (ObjectUtils.isEmpty(getMethodParameters())) {return EMPTY_ARGS;}//入参的包装类,里面包装了参数类型,参数名称,参数注解等等信息MethodParameter[] parameters = getMethodParameters();Object[] args = new Object[parameters.length];for (int i = 0; i < parameters.length; i++) {MethodParameter parameter = parameters[i];//设置参数名称解析器parameter.initParameterNameDiscovery(this.parameterNameDiscoverer);args[i] = findProvidedArgument(parameter, providedArgs);if (args[i] != null) {continue;}//典型的策略模式,根据parameter能否找到对应参数的处理类,能找到就返回trueif (!this.resolvers.supportsParameter(parameter)) {throw new IllegalStateException(formatArgumentError(parameter, "No suitable resolver"));}try {//具体参数值解析过程,重点看看args[i] = this.resolvers.resolveArgument(parameter, mavContainer, request, this.dataBinderFactory);}catch (Exception ex) {// Leave stack trace for later, exception may actually be resolved and handled..if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { String error = ex.getMessage(); if (error != null && !error.contains(parameter.getExecutable().toGenericString())) { logger.debug(formatArgumentError(parameter, error)); }}throw ex;}}return args;} |
参数、返回值解析
因为参数类型非常多,同时还会伴随各种注解,如:@RequestBody、@RequestParam、@PathVariable等,所以参数解析的工作是非常繁杂的,同时还要考虑到扩展性,所以SpringMVC依然采用了策略模式来完成对各种参数类型的解析绑定,其顶层接口就是HandlerMethodArgumentResolver,而默认SpringMVC提供的解析方式就高达20多种:

上面是类图,读者可根据自己熟悉的参数类型找到对应的类进行分析,最核心的还是要掌握这里的设计思想。
接着方法调用完成后就是对返回值的处理,同样的,返回值类型也是非常多,也可以使用各种注解标注,所以也是使用策略模式实现,其顶层接口是HandlerMethodReturnValueHandler,实现类如下:

调用完成之后就是执行后续操作了:执行中置过滤器、处理全局异常、视图渲染以及执行后置过滤器,这些与主流程没有太大关系,本篇不展开分析了,最后是MVC的执行时序图:
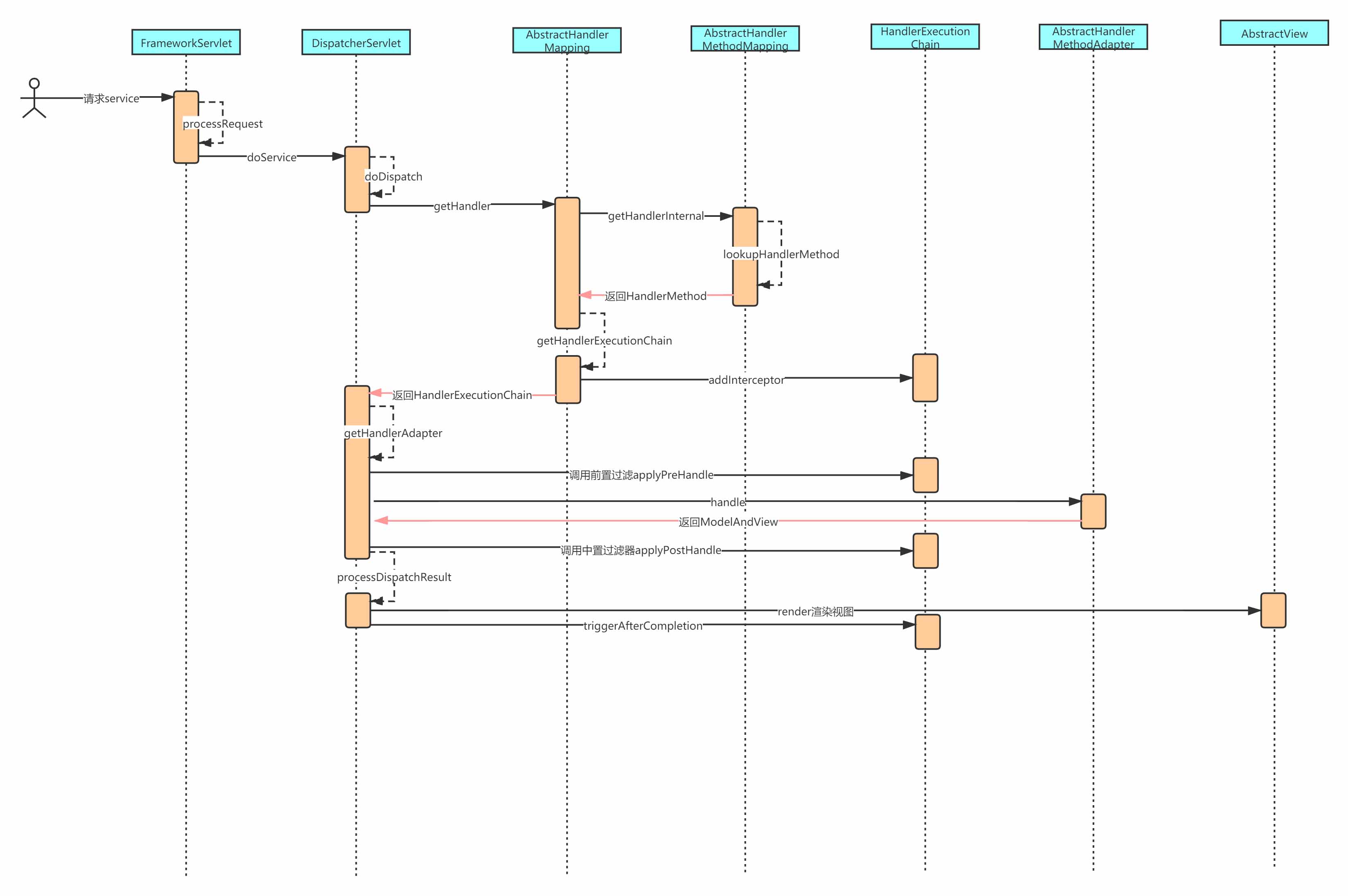
总结
本篇是Spring核心原理系列的最后一篇,前前后后花了一个月时间,终于从宏观上大致上理解了Spring的实现原理和运行机制,明白了之前项目中一些坑是如何产生的,最主要的是学到设计模式的运用以及如何利用Spring的一些常用的扩展点进行自定义扩展。但对于Spring这个庞大的体系来说,还有很多是要去理解学习的,尤其是设计思想,只有长期琢磨才能深刻的理解掌握。在我之前的文章中包括本篇还有很多没分析到的细节,在后面我会不定期分享出来。希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/l6108003/article/details/106770028















