由于项目需要,需要对二进制文件进行读写、转换。
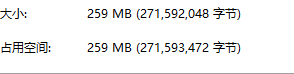
文件说明:由其他程序得到的二进制文件,文件内容为:包含23543个三角形、13270个顶点的三角网所对应的721组流速矢量(u、v)文件,通俗些说,一条数据包含两个双精度型的数值,每组数组包含23543条数据,如果以一个双精度数值为单位,则总共有23543 * 721 * 2 =33,949,006条数据。由Fortran程序以每 8 Byte存储一个数值的二进制文件存储,最终文件大小为下图所示:
测试:从该文件读出数据之后,转换为十进制,存储到另一个文件中。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
|
/** * 针对大文件存储,请依次调用beginSave、AddSave、endSave。 * * @author CK * */public class DataUtil { DataOutputStream BinaryOut=null; BufferedWriter TextOut=null; String FilePath=null; enum SaveFileType{Text,Binary}; SaveFileType SaveFileType; /** * double转byte[] * * @param d * @return */ public static byte[] double2Bytes(double d) { long value = Double.doubleToRawLongBits(d); byte[] byteRet = new byte[8]; for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { byteRet[i] = (byte) ((value >> 8 * i) & 0xff); } return byteRet; } /** * byte[]转double * * @param arr * @return */ public static double bytes2Double(byte[] arr) { long value = 0; for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) { value |= ((long) (arr[i] & 0xff)) << (8 * i); } return Double.longBitsToDouble(value); } /** * 大型数据存储之开始存储 * @param FilePath 文件路径 * @param saveFileType 保存的文件类型,文本文件、双精度所存的二进制文件 * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean BeginSave(String FilePath,SaveFileType saveFileType) throws IOException { if (FilePath == "" || FilePath == null) { System.out.println("the SavePath is null."); return false; } this.FilePath=FilePath; this.SaveFileType=saveFileType; File dataFile = new File(FilePath); if (!dataFile.getParentFile().exists()) { dataFile.getParentFile().mkdirs(); } if (dataFile.exists()) { dataFile.delete(); } dataFile.createNewFile(); switch(this.SaveFileType){ case Text: TextOut= new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dataFile,true)); break; case Binary: BinaryOut = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dataFile,true)); break; default: break; } return true; }/** * 大型文件存储之追加存储 * @param DataStr 若是文本存储则无要求,若是双精度的二进制文件,以若干空格隔开 * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean AddSave(String DataStr) throws IOException{ switch(this.SaveFileType){ case Text: this.TextOut.append(DataStr); break; case Binary: DataStr=DataStr.trim(); String[] dataArray=DataStr.split("\\s+"); for(int i=0;i<dataArray.length;i++){ this.BinaryOut.write(double2Bytes(Double.parseDouble(dataArray[i]))); } break; default: break; } return true; } /** * 大型文件存储之结束保存,清空缓存、关闭文件。 * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean EndSave() throws IOException{ switch(this.SaveFileType){ case Text: this.TextOut.flush(); this.TextOut.close(); break; case Binary: this.BinaryOut.flush(); this.BinaryOut.close(); break; default: break; } return true; } /** * 将字符串保存为文本文件(一次完成) * * @param DataStr * 文件内容 * @param SavePath * 文件路径,包含文件名、后缀 * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean saveTextFile(String DataStr, String SavePath) throws IOException { if (DataStr == "" || DataStr == null) { System.out.println("the dataStr is null."); return false; } if (SavePath == "" || SavePath == null) { System.out.println("the SavePath is null."); return false; } File dataFile = new File(SavePath); if (!dataFile.getParentFile().exists()) { dataFile.getParentFile().mkdirs(); } if (dataFile.exists()) { dataFile.delete(); } dataFile.createNewFile(); BufferedWriter out; out = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(dataFile)); out.append(DataStr); out.flush(); out.close(); return true; } /** * 双精度存为二进制数据(一次存储) * * @param DataStr 双精度数据组成的字符串,以若干空格隔开 * @param OutputPath * @return * @throws IOException */ public boolean saveBinaryFile(String DataStr, String OutputPath) throws IOException { if (DataStr == "" || DataStr == null) { System.out.println("the dataStr is null."); return false; } if (OutputPath == "" || OutputPath == null) { System.out.println("the OutputPath is null."); return false; } File dataFile = new File(OutputPath); if (!dataFile.getParentFile().exists()) { dataFile.getParentFile().mkdirs(); } if (dataFile.exists()) { dataFile.delete(); } dataFile.createNewFile(); DataOutputStream out; out = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(dataFile)); // 数据处理 DataStr=DataStr.trim(); String[] dataArray=DataStr.split("\\s+"); for(int i=0;i<dataArray.length;i++){ out.write(double2Bytes(Double.parseDouble(dataArray[i]))); } out.flush(); out.close(); return true; }} |
代码说明:其中byte[]与double互转为在互联网上查到的方法,具体是哪位大神的我忘记了,在这里为了记录就贴出来啦,上述代码包含了处理小型文件时,将所有内容存在缓存中,之后再一次性写入文本文件、二进制文件中的方法,还包含了对较大型文件的读写方法,下面是自己的一个读写测试。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
/** * 测试二进制大文件读写(200M左右) * @author ck * */public class FileTest { static String inputFilePath=""; //输入文件路径,包含文件名后缀 static String outputFilePath=""; //输出文件名,包含文件名后缀 public static void file2file() throws IOException{ DataUtil dataUtil=new DataUtil(); DataInputStream br=new DataInputStream( new BufferedInputStream( new FileInputStream(inputFilePath))); dataUtil.BeginSave(outputFilePath, SaveFileType.Text); //初始化,创建文件,采用文件追加存储的思路 byte[] oneData=new byte[8]; int i=0,count =0 ; while(br.read(oneData, 0, 8)!=-1){ i=i+1; dataUtil.AddSave(String.valueOf(DataUtil.bytes2Double(oneData))); if(i/23543==0){ count++; System.out.println(count+"\n"); } } dataUtil.EndSave(); //将还在缓存中的数据写入到文件中,关闭文件。 }} |
此次测试代码很快就run完了,但是输出文件的生成大概用了近半分钟(刻意秒表计时了一次),尝试用一次性读写的办法,卡很久,也没有出结果。所得的十进制文本文件,大小为这么多:

我想,原来Fortran程序作者的初衷应该是觉得二进制存储比十进制节省空间吧,事实上也确实节省了一半多的空间。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持服务器之家。
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/ForRickHuan/p/6421796.html















