在.NET Framework4.5框架、C#5.0语法中,通过async和await两个关键字,引入了一种新的基于任务的异步编程模型(TAP)。在这种方式下,可以通过类似同步方式编写异步代码,极大简化了异步编程模型。
用法:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public async Task<int> GetDotNetCountAsync(){ // Suspends GetDotNetCount() to allow the caller (the web server) // to accept another request, rather than blocking on this one. var html = await _httpClient.GetStringAsync("https://dotnetfoundation.org"); return Regex.Matches(html, @"\.NET").Count;} |
要点!!!
1.“async”用来标记一个方法为异步方法,异步方法体内需结合“await”关键字使用,如果没有await,则该方法等同于一个普通方法。异步方法命名规则通常以Async结尾。
2.“await”关键字只能在异步方法中使用。
3.当在async异步方法中遇到await操作时,await会阻塞该异步方法不继续往下执行,并将该异步方挂起,将控制权转到该异步方法的调用者手中。
4.异步方法的调用者获得控制权之后:
1)如果调用者需要使用异步方法的返回结果,则继续等待异步方法执行完毕,再继续往下执行。
2)如果调用者不关心异步方法的返回结果,则继续往下执行。
场景一:async方法中未使用await
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("执行前Main.....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤① GetResultAsync(); Console.WriteLine("执行结束Main....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤② Console.ReadKey(); } async static Task<int> GetResultAsync() { Console.WriteLine("执行前GetResult.....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤③ Task.Delay(3000).Wait(); Console.WriteLine("执行结束GetResult.....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤④ return 10; } |
执行结果:步骤① ——>步骤③——>步骤④——>步骤②
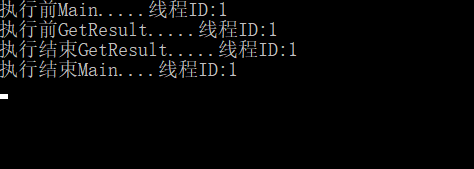
结果分析:
我们会发现,主函数Main调用异步方法GetResultAsync时,由于异步方法缺少“await”关键字,主函数需等异步方法步骤3,4全部执行结束后再继续执行步骤2,执行顺序完全和同步方法执行顺序一致;
并且异步方法会给出语法提示:缺少“await”关键字
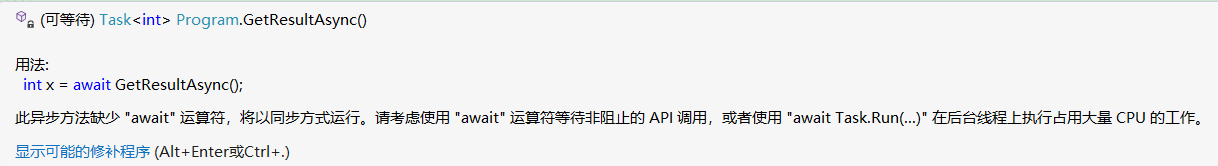
场景2:异步方法体内遇到await之后,立即将控制权转到调用者手中
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("执行前Main.....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤① GetResultAsync(); Console.WriteLine("执行结束Main....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤② Console.ReadKey(); } async static Task<int> GetResultAsync() { Console.WriteLine("执行前GetResult.....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤③ await Task.Delay(3000); Console.WriteLine("执行结束GetResult.....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤④ return 10; } |
执行结果:步骤① ——>步骤③——>步骤②——>步骤④
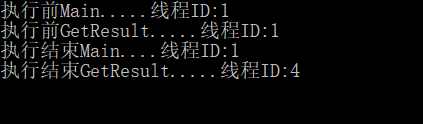
结果分析:
我们会发现,主函数Main调用异步方法GetResultAsync,在遇到异步方法中“await”关键字时
1)阻塞了当前异步方法并立即将控制权转交给调用者主函数Main
2)主函数获得控制权后继续执行方法体内步骤2,GetResultAsync方法则异步执行(等待异步操作结束之后执行步骤4)。
场景3:异步方法体内遇到await之后,立即将控制权转到调用者手中,调用者需等待异步方法返回结果
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
static void Main(string[] args) { Console.WriteLine("执行前Main.....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤① Task<int> res = GetResultAsync(); Console.WriteLine("执行结束Main....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤② Console.WriteLine("执行结果:" + res.Result + "....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤③ Console.ReadKey(); } async static Task<int> GetResultAsync() { Console.WriteLine("执行前GetResult.....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤④ await Task.Delay(3000); Console.WriteLine("执行结束GetResult.....线程ID:" + Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId.ToString());//步骤⑤ return 10; } |
执行结果:步骤① ——>步骤④——>步骤②——>步骤⑤——>步骤③
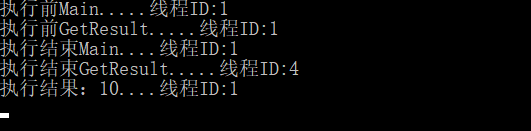
结果分析:
我们会发现,主函数Main调用异步方法GetResultAsync,在遇到异步方法中“await”关键字时
1)阻塞了当前异步方法并立即将控制权转交给调用者主函数Main
2)主函数获得控制权后继续执行方法体内步骤2和步骤3,GetResultAsync方法则异步执行。
3)当主函数执行步骤3时,由于步骤3需要打印异步方法的返回结果,故需要等待异步方法结束才能继续。所以需先执行步骤5,然后再继续执行步骤3。
最后,异步编程的时候我们通常会结合Task来使用
到此这篇关于ASP.Net中的async+await异步编程的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关ASP.Net async+await异步编程内容请搜索服务器之家以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持服务器之家!
原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/chenxf1117/p/13523533.html